An Evaluation of the Performance, Patient Acceptability, and Feasibility of a Point-of-Care HIV-Syphilis Assay in an Urban Emergency Department
- PMID: 38722756
- PMCID: PMC11392641
- DOI: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001995
An Evaluation of the Performance, Patient Acceptability, and Feasibility of a Point-of-Care HIV-Syphilis Assay in an Urban Emergency Department
Abstract
Background: Point-of-care (POC) tests for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) permit delivery of results during the patient's emergency department (ED) encounter. We evaluated performance, patient acceptability, and feasibility of a new duplex POC test, Chembio Dual Path Platform HIV-Syphilis Assay, in an urban ED setting.
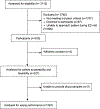
Methods: Convenience sampling approach prioritizing those considered at increased risk for an STI and/or with a history of HIV. For the performance evaluation, participants were tested for HIV/syphilis with the Chembio POC assay and the reference laboratory tests; sensitivity and specificity were determined. For the patient acceptability evaluation, participants completed pre- and post-user surveys. For the feasibility evaluation, ED clinical technicians completed a survey evaluating their perceptions regarding feasibility of use of this POC test.
Results: A total of 327 patients were consented and enrolled. The diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of the Chembio POC assay for HIV were 96.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 90.1%-99.3%) and 99.6% (95% CI, 97.7%-100.0%), respectively, and for syphilis, the values were 93.9% (95% CI, 85.0%-98.3%) and 99.6% (95% CI, 97.9%-100.0%), respectively. Regarding patient acceptability, 87% trusted the result, and 93% reported that they were more likely to seek treatment if they received a positive STI test result in the ED rather than after the ED visit. Regarding feasibility, 90% of the technicians reported that they would recommend using the test in EDs.
Conclusions: The Chembio Dual Path Platform HIV-Syphilis POC Assay had excellent performance characteristics when evaluated in an ED population, as well as high perceived acceptability from patients, and feasibility for ED use from clinical technicians. The test may have utility for HIV-syphilis screening among high-risk ED patients.
Copyright © 2024 American Sexually Transmitted Diseases Association. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest and Sources of Funding: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. This study was funded by U54EB007958, National Institute of Biomedical Imagining and Bioengineering, National Institutes of Health. Chembio Diagnostic Systems provided diagnostic test kits.
Figures
References
-
- Seballos S, Lopez R, Hustey F, et al. Cotesting for Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Sexually Transmitted Infections in the Emergency Department. Sex Transm Dis. 2022;49(8):546–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical