Declining Antibody Affinity Over Time After Human Vaccination With a Plasmodium falciparum Merozoite Vaccine Candidate
- PMID: 38723177
- PMCID: PMC11420798
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiae259
Declining Antibody Affinity Over Time After Human Vaccination With a Plasmodium falciparum Merozoite Vaccine Candidate
Abstract
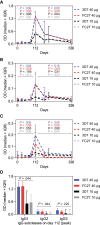
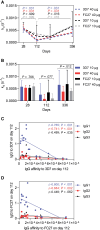
Maintaining high-affinity antibodies after vaccination may be important for long-lasting immunity to malaria, but data on induction and kinetics of affinity is lacking. In a phase 1 malaria vaccine trial, antibody affinity increased following a second vaccination but declined substantially over 12 months, suggesting poor maintenance of high-affinity antibodies.
Clinical trials registration: Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry ACTRN12607000552482.
Keywords: affinity maintenance; antibody; antibody affinity; malaria; malaria vaccine.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts of interest. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . World malaria report 2023. https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/reports/world-malaria.... Accessed 21 February 2024.
-
- Vogel G. Second malaria vaccine gets WHO green light. Science 2023; 382:16–7. - PubMed
-
- Breukels MA, Jol-van der Zijde E, van Tol MJ, Rijkers GT. Concentration and avidity of anti-Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) antibodies in serum samples obtained from patients for whom Hib vaccination failed. Clin Infect Dis 2002; 34:191–7. - PubMed
-
- Hetherington SV, Lepow ML. Correlation between antibody affinity and serum bactericidal activity in infants. J Infect Dis 1992; 165:753–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

