Chemoradiotherapy-induced ACKR2+ tumor cells drive CD8+ T cell senescence and cervical cancer recurrence
- PMID: 38723624
- PMCID: PMC11148771
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101550
Chemoradiotherapy-induced ACKR2+ tumor cells drive CD8+ T cell senescence and cervical cancer recurrence
Abstract
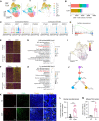
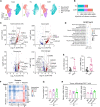
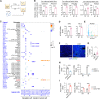
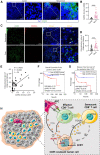
Tumor recurrence after chemoradiotherapy is challenging to overcome, and approaches to predict the recurrence remain elusive. Here, human cervical cancer tissues before and after concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT) analyzed by single-cell RNA sequencing reveal that CCRT specifically promotes CD8+ T cell senescence, driven by atypical chemokine receptor 2 (ACKR2)+ CCRT-resistant tumor cells. Mechanistically, ACKR2 expression is increased in response to CCRT and is also upregulated through the ligation of CC chemokines that are produced by activated myeloid and T cells. Subsequently, ACKR2+ tumor cells are induced to produce transforming growth factor β to drive CD8+ T cell senescence, thereby compromising antitumor immunity. Moreover, retrospective analysis reveals that ACKR2 expression and CD8+ T cell senescence are enhanced in patients with cervical cancer who experienced recurrence after CCRT, indicating poor prognosis. Overall, we identify a subpopulation of CCRT-resistant ACKR2+ tumor cells driving CD8+ T cell senescence and tumor recurrence and highlight the prognostic value of ACKR2 and CD8+ T cell senescence for chemoradiotherapy recurrence.
Keywords: ACKR2; CD8(+) T cell senescence; cervical cancer; single-cell RNA sequencing; tumor recurrence.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Peters W.A., 3rd, Liu P.Y., Barrett R.J., 2nd, Stock R.J., Monk B.J., Berek J.S., Souhami L., Grigsby P., Gordon W., Jr., Alberts D.S. Concurrent chemotherapy and pelvic radiation therapy compared with pelvic radiation therapy alone as adjuvant therapy after radical surgery in high-risk early-stage cancer of the cervix. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000;18:1606–1613. doi: 10.1200/jco.2000.18.8.1606. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

