A clinical-radiomics nomogram based on dual-layer spectral detector CT to predict cancer stage in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 38725034
- PMCID: PMC11080083
- DOI: 10.1186/s40644-024-00700-z
A clinical-radiomics nomogram based on dual-layer spectral detector CT to predict cancer stage in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of radiomics signatures derived from polyenergetic images (PEIs) and virtual monoenergetic images (VMIs) obtained through dual-layer spectral detector CT (DLCT). Moreover, it sought to develop a clinical-radiomics nomogram based on DLCT for predicting cancer stage (early stage: stage I-II, advanced stage: stage III-IV) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
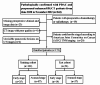
Methods: A total of 173 patients histopathologically diagnosed with PDAC and who underwent contrast-enhanced DLCT were enrolled in this study. Among them, 49 were in the early stage, and 124 were in the advanced stage. Patients were randomly categorized into training (n = 122) and test (n = 51) cohorts at a 7:3 ratio. Radiomics features were extracted from PEIs and 40-keV VMIs were reconstructed at both arterial and portal venous phases. Radiomics signatures were constructed based on both PEIs and 40-keV VMIs. A radiomics nomogram was developed by integrating the 40-keV VMI-based radiomics signature with selected clinical predictors. The performance of the nomogram was assessed using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, calibration curves, and decision curves analysis (DCA).
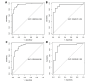
Results: The PEI-based radiomics signature demonstrated satisfactory diagnostic efficacy, with the areas under the ROC curves (AUCs) of 0.92 in both the training and test cohorts. The optimal radiomics signature was based on 40-keV VMIs, with AUCs of 0.96 and 0.94 in the training and test cohorts. The nomogram, which integrated a 40-keV VMI-based radiomics signature with two clinical parameters (tumour diameter and normalized iodine density at the portal venous phase), demonstrated promising calibration and discrimination in both the training and test cohorts (0.97 and 0.91, respectively). DCA indicated that the clinical-radiomics nomogram provided the most significant clinical benefit.
Conclusions: The radiomics signature derived from 40-keV VMI and the clinical-radiomics nomogram based on DLCT both exhibited exceptional performance in distinguishing early from advanced stages in PDAC, aiding clinical decision-making for patients with this condition.
Keywords: Cancer stage; Dual-layer spectral detector CT; Nomogram; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; Radiomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Radiomics analysis of dual-layer detector spectral CT-derived iodine maps for predicting Ki-67 PI in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Apr 17;25(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01664-7. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40247246 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-layer spectral CT improves image quality of multiphasic pancreas CT in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Eur Radiol. 2020 Jan;30(1):394-403. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06337-y. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31312889
-
Development of a CT radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of Ki-67 index in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a two-center retrospective study.Eur Radiol. 2024 May;34(5):2934-2943. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10393-w. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37938382
-
The preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis of resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using dual-layer spectral computed tomography.Eur Radiol. 2025 May;35(5):2692-2701. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-11143-2. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39448418
-
The clinical applications of dual-layer spectral detector CT in digestive system diseases.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jun;35(6):3547-3557. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-11290-6. Epub 2024 Dec 19. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39699679 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation Between Fatty Pancreas Disease and Pancreatic Diseases, Perioperative Complications of Pancreatic Surgery.Cancer Manag Res. 2025 Mar 29;17:723-730. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S508567. eCollection 2025. Cancer Manag Res. 2025. PMID: 40177416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nomogram combining dual-energy computed tomography features and radiomics for differentiating parotid warthin tumor from pleomorphic adenoma: a retrospective study.Front Oncol. 2025 Mar 4;15:1505385. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1505385. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40104493 Free PMC article.
-
DCE-MRI quantitative analysis and MRI-based radiomics for predicting the early efficacy of microwave ablation in lung cancers.Cancer Imaging. 2025 Mar 10;25(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s40644-025-00851-7. Cancer Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40065426 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics analysis of dual-layer detector spectral CT-derived iodine maps for predicting Ki-67 PI in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Apr 17;25(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01664-7. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40247246 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics-clinical nomogram for preoperative tumor-node-metastasis staging prediction in breast cancer patients using dynamic enhanced magnetic resonance imaging.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 30;14(3):1836-1848. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1559. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40225004 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

