Multi-Omics profiling identifies aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 as a critical mediator in the crosstalk between Treg-mediated immunosuppression microenvironment and hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38725845
- PMCID: PMC11077362
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.93075
Multi-Omics profiling identifies aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 as a critical mediator in the crosstalk between Treg-mediated immunosuppression microenvironment and hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
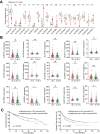
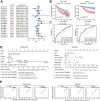
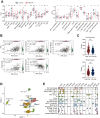
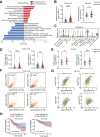
Dysregulation of the aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) family has been implicated in various pathological conditions, including cancer. However, a systematic evaluation of ALDH alterations and their therapeutic relevance in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains lacking. Herein, we found that 15 of 19 ALDHs were transcriptionally dysregulated in HCC tissues compared to normal liver tissues. A four gene signature, including ALDH2, ALDH5A1, ALDH6A1, and ALDH8A1, robustly predicted prognosis and defined a high-risk subgroup exhibiting immunosuppressive features like regulatory T cell (Tregs) infiltration. Single-cell profiling revealed selective overexpression of tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 18 (TNFRSF18) on Tregs, upregulated in high-risk HCC patients. We identified ALDH2 as a tumor suppressor in HCC, with three novel phosphorylation sites mediated by protein kinase C zeta that enhanced enzymatic activity. Mechanistically, ALDH2 suppressed Tregs differentiation by inhibiting β-catenin/TGF-β1 signaling in HCC. Collectively, our integrated multi-omics analysis defines an ALDH-Tregs-TNFRSF18 axis that contributes to HCC pathogenesis and represents potential therapeutic targets for this aggressive malignancy.
Keywords: ALDH2; Liver cancer; Metabolic disturbance; Regulatory T cells; TNFRSF18 (GITR).
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
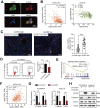
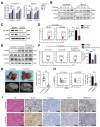
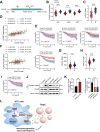
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE. et al. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Hu B, Yu M, Ma X. et al. Interferon-a potentiates anti-PD-1 efficacy by remodeling glucose metabolism in the hepatocellular carcinoma microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2022;12:1718–1741. - PubMed
-
- Wong AM, Ding X, Wong AM. et al. Unique molecular characteristics of NAFLD-associated liver cancer accentuate β-catenin/TNFRSF19-mediated immune evasion. J Hepatol. 2022;77:410–423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

