Uncovering a Novel Functional Interaction Between Adult Hepatic Progenitor Cells, Inflammation and EGFR Signaling During Bile Acids-Induced Injury
- PMID: 38725853
- PMCID: PMC11077361
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.90645
Uncovering a Novel Functional Interaction Between Adult Hepatic Progenitor Cells, Inflammation and EGFR Signaling During Bile Acids-Induced Injury
Abstract
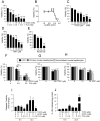
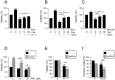
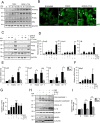
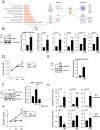
Chronic cholestatic damage is associated to both accumulation of cytotoxic levels of bile acids and expansion of adult hepatic progenitor cells (HPC) as part of the ductular reaction contributing to the regenerative response. Here, we report a bile acid-specific cytotoxic response in mouse HPC, which is partially impaired by EGF signaling. Additionally, we show that EGF synergizes with bile acids to trigger inflammatory signaling and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in HPC. Aiming at understanding the impact of this HPC specific response on the liver microenvironment we run a proteomic analysis of HPC secretome. Data show an enrichment in immune and TGF-β regulators, ECM components and remodeling proteins in HPC secretome. Consistently, HPC-derived conditioned medium promotes hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation and macrophage M1-like polarization. Strikingly, EGF and bile acids co-treatment leads to profound changes in the secretome composition, illustrated by an abolishment of HSC activating effect and by promoting macrophage M2-like polarization. Collectively, we provide new specific mechanisms behind HPC regulatory action during cholestatic liver injury, with an active role in cellular interactome and inflammatory response regulation. Moreover, findings prove a key contribution for EGFR signaling jointly with bile acids in HPC-mediated actions.
Keywords: Bile acids; EGFR; Hepatic Progenitor Cell; Inflammation; Liver Disease; Secretome.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Marcellin P, Kutala BK. Liver diseases: A major, neglected global public health problem requiring urgent actions and large-scale screening. Liver Int. 2018;38(Suppl 1):2–6. - PubMed
-
- Hirschfield GM, Heathcote EJ, Gershwin ME. Pathogenesis of cholestatic liver disease and therapeutic approaches. Gastroenterology. 2010;139:1481–96. - PubMed
-
- Jansen PL, Ghallab A, Vartak N, Reif R, Schaap FG, Hampe J. et al. The ascending pathophysiology of cholestatic liver disease. Hepatology. 2017;65:722–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

