Downregulation of TRIB3 enhances the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to amino acid deprivation by suppressing AKT activation
- PMID: 38726284
- PMCID: PMC11076249
- DOI: 10.62347/GLSY2976
Downregulation of TRIB3 enhances the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to amino acid deprivation by suppressing AKT activation
Abstract
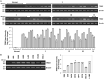
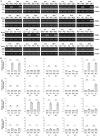
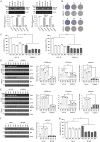
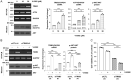
Tribbles pseudokinase 3 (TRIB3), a member of the mammalian Tribbles family, is implicated in multiple biological processes. This study aimed to investigate the biological functions of TRIB3 in lung cancer and its effect on amino acid-deprived lung cancer cells. TRIB3 mRNA expression was elevated in lung cancer tissues and cell lines compared to normal lung tissues and cells. TRIB3 knockdown markedly reduced the viability and proliferation of H1299 lung cancer cells. Deprivation of amino acids, particularly arginine, glutamine, lysine, or methionine, strongly increased TRIB3 expression via ATF4 activation in H1299 lung cancer cells. Knockdown of TRIB3 led to transcriptional downregulation of ATF4 and reduced AKT activation induced by amino acid deprivation, ultimately increasing the sensitivity of H1299 lung cancer cells to amino acid deprivation. Additionally, TRIB3 knockdown enhanced the sensitivity of H1299 cells to V-9302, a competitive antagonist of transmembrane glutamine flux. These results suggest that TRIB3 is a pro-survival regulator of cell viability in amino acid-deficient tumor microenvironments and a promising therapeutic target for lung cancer treatment.
Keywords: AKT; ATF4; TRIB3; amino acid depletion; lung cancer.
AJCR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Kiss-Toth E, Velasco G, Pear WS. Tribbles at the cross-roads. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015;43:1049–1050. - PubMed
-
- Kiss-Toth E. Tribbles: ‘puzzling’ regulators of cell signalling. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011;39:684–687. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
