Extrahepatic malignancies and antiviral drugs for chronic hepatitis B: A nationwide cohort study
- PMID: 38726505
- PMCID: PMC11261230
- DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0055
Extrahepatic malignancies and antiviral drugs for chronic hepatitis B: A nationwide cohort study
Abstract
Background/aims: Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is related to an increased risk of extrahepatic malignancy (EHM), and antiviral treatment is associated with an incidence of EHM comparable to controls. We compared the risks of EHM and intrahepatic malignancy (IHM) between entecavir (ETV) and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) treatment.
Methods: Using data from the National Health Insurance Service of Korea, this nationwide cohort study included treatment-naïve CHB patients who initiated ETV (n=24,287) or TDF (n=29,199) therapy between 2012 and 2014. The primary outcome was the development of any primary EHM. Secondary outcomes included overall IHM development. E-value was calculated to assess the robustness of results to unmeasured confounders.
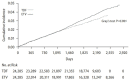
Results: The median follow-up duration was 5.9 years, and all baseline characteristics were well balanced after propensity score matching. EHM incidence rate differed significantly between within versus beyond 3 years in both groups (P<0.01, Davies test). During the first 3 years, EHM risk was comparable in the propensity score-matched cohort (5.88 versus 5.84/1,000 person-years; subdistribution hazard ratio [SHR]=1.01, 95% confidence interval [CI]=0.88-1.17, P=0.84). After year 3, however, TDF was associated with a significantly lower EHM incidence compared to ETV (4.92 versus 6.91/1,000 person-years; SHR=0.70, 95% CI=0.60-0.81, P<0.01; E-value for SHR=2.21). Regarding IHM, the superiority of TDF over ETV was maintained both within (17.58 versus 20.19/1,000 person-years; SHR=0.88, 95% CI=0.81-0.95, P<0.01) and after year 3 (11.45 versus 16.20/1,000 person-years; SHR=0.68, 95% CI=0.62-0.75, P<0.01; E-value for SHR=2.30).
Conclusion: TDF was associated with approximately 30% lower risks of both EHM and IHM than ETV in CHB patients after 3 years of antiviral therapy.
Keywords: Antiviral treatment; Entecavir; Hepatitis B virus; Non-liver cancer; Tenofovir.
Conflict of interest statement
Moon Haeng Hur: Nothing to declare; Dong Hyeon Lee: Nothing to declare; Jeong-Hoon Lee: Receives research grants from Yuhan Pharmaceuticals and GreenCross Cell, lecture fees from GreenCross Cell, Daewoong Pharmaceuticals, and Gilead Korea; Mi-Sook Kim: Nothing to declare; Jeayeon Park: Nothing to declare; Hyunjae Shin: Nothing to declare; Sung Won Chung: Nothing to declare; to declare; Heejoon Jang: Nothing to declare; Yun Bin Lee: Receives research grants from Samjin Pharmaceuticals and Yuhan Pharmaceuticals; Su Jong Yu: Receives research grants from Yuhan Pharmaceuticals and Daewoong Pharmaceuticals; Sang Hyub Lee: Nothing to declare; Yong Jin Jung: Nothing to declare; Yoon Jun Kim: Receives research grants from BTG, Boston Scientific, AstraZeneca, Gilead Sciences, Samjin, BL&H, and Bayer, and lecture fees from Roche, Abbvie, Eisai, Boston Scientific, BMS, BTG, Bayer, MSD, Novo Nordisk, Green Cross Cell, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Gilead; Jung-Hwan Yoon: Receives research grants from Bayer, Daewoong Pharmaceutical, and Bukwang Pharmaceutical.
Figures


Comment in
-
Nucleos(t)ide analog therapy of chronic hepatitis B and extrahepatic cancer risk: Is tenofovir better than entecavir?: Editorial on "Extrahepatic malignancies and antiviral drugs for chronic hepatitis B: A nationwide cohort study".Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024 Oct;30(4):718-720. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0519. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38973180 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390:1211–1259. - PMC - PubMed
-
- European Association For The Study Of The Liver EASL 2017 clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 2017;67:370–398. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

