Capivasertib in combination with enzalutamide for metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer after docetaxel and abiraterone: Results from the randomized phase II RE-AKT trial
- PMID: 38729054
- PMCID: PMC11181075
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2024.114103
Capivasertib in combination with enzalutamide for metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer after docetaxel and abiraterone: Results from the randomized phase II RE-AKT trial
Abstract
Background: PTEN loss and aberrations in PI3K/AKT signaling kinases associate with poorer response to abiraterone acetate (AA) in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). In this study, we assessed antitumor activity of the AKT inhibitor capivasertib combined with enzalutamide in mCRPC with prior progression on AA and docetaxel.
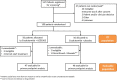
Methods: This double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized phase 2 trial, recruited men ≥ 18 years with progressing mCRPC and performance status 0-2 from 15 UK centers. Randomized participants (1:1) received enzalutamide (160 mg orally, once daily) with capivasertib (400 mg)/ placebo orally, twice daily on an intermittent (4 days on, 3 days off) schedule. Primary endpoint was composite response rate (RR): RECIST 1.1 objective response, ≥ 50 % PSA decrease from baseline, or circulating tumor cell count conversion (from ≥ 5 at baseline to < 5 cells/7.5 mL). Subgroup analyses by PTENIHC status were pre-planned.
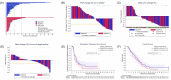
Results: Overall, 100 participants were randomized (50:50); 95 were evaluable for primary endpoint (47:48); median follow-up was 43 months. RR were 9/47 (19.1 %) enzalutamide/capivasertib and 9/48 (18.8 %) enzalutamide/placebo (absolute difference 0.4 % 90 %CI -12.8 to 13.6, p = 0.58), with similar results in the PTENIHC loss subgroup. Irrespective of treatment, OS was significantly worse for PTENIHC loss (10.1 months [95 %CI: 4.6-13.9] vs 14.8 months [95 %CI: 10.8-18]; p = 0.02). Most common treatment-emergent grade ≥ 3 adverse events for the combination were diarrhea (13 % vs 2 %) and fatigue (10 % vs 6 %).
Conclusions: Combined capivasertib/enzalutamide was well tolerated but didn't significantly improve outcomes from abiraterone pre-treated mCRPC.
Keywords: AKT-inhibitor; Enzalutamide; PTEN; Phase II randomized trial; Prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: JdB reports advisory board fees from many companies including Acai Therapeutics, Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Astellas, Bayer, Bioxcel Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cellcentric, Crescendo, Daiichi, Dark Blue Therapeutics, Eisai, Genentech/Roche, Genmab, GSK, Harpoon, ImCheck Therapeutics, Janssen, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Menarini/Silicon Biosystems, MetaCurUm, Myricx, Novartis, Nurix Therapeutics, Oncternal, Orion, Pfizer, Qiagen, Sanofi Aventis, Sierra Oncology, Taiho, Takeda, Tango Therapeutics, Terumo, Vertex Pharmaceuticals. He is an employee of The ICR, which have received funding or other support for his research work from Acai Therapeutics, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Astellas, Bayer, Cellcentric, Crescendo, Daiichi, Genentech, Genmab, GSK, Harpoon, Immunic Therapeutics, Janssen, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Menarini/Silicon Biosystems, MetaCurUm, Myricx, Nurix Therapeutics, Oncternal, Orion, Pfizer, Qiagen, Sanofi Aventis, Sierra Oncology, Taiho, Vertex Pharmaceuticals. The ICR have a commercial interest in abiraterone, PARP inhibition in DNA repair defective cancers and PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitors (no personal income). JDB was named as an inventor, with no financial interest for patent 8,822,438, submitted by Janssen that covers the use of abiraterone acetate with corticosteroids. EH reports that their institution has received an Investigator Initiated Research grant (IIR) from AstraZeneca for the central coordination of the trial. EH reports grants received by their institution as contribution to support central trial costs for non-commercial trials from Accuray, Varian Medical Systems, AstraZeneca, Janssen-Cilag, Bayer, Roche Products, and Merck Sharp and Dohm. SJ reports advisory boards and speaker fees received from AAA/Novartis, Accord, Astellas, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Boston Scientific, Janssen and Pfizer, as well as consultancy fees received from Boston Scientific and BXT Nanotherapy. SJ also reports conferences travel received from Bayer and Janssen. AJB reports honoraria from Janssen-Cilag, consulting or advisory roles from Roche, Astellas Medivation, Janssen Oncology, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Bayer Schering Pharma, Bristol-Myers-Squib, Merck Serono and Pfizer. AJB also reports speakers’ fees received from Bayer, Janssen Oncology and Pfizer. RJ reports honoraria from Astellas Pharma, Janssen, AstraZeneca, MSD Oncology, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Novartis, Ipsen, Bayer, Roche/Genentech, Merck Serono, Eisai, WebMD, Advanced Accelerator Applications/Novartis and Elsevier. RJ also reports speakers’ fees received from Merck Serono, Pfizer, Janssen, Astellas Pharma, MSD Oncology, AstraZeneca, Ipsen, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene and Bayer. RJ also reports research Funding received from Roche (Inst), Astellas Pharma (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst), Exelixis (Inst), Clovis Oncology (Inst) and Bayer (Inst), as well as travel, accommodations and expenses received from Ipsen, Bayer, Janssen, Astellas Pharma, MSD, Merck Serono and Pfizer. PR, NP, LF, AE, SM, PF, JG, JN, RR, BG, DR, IF, SC, CB, AF, MC, SC, ZM, CR, UMC, PH, PS, EC and DML have no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Bray F., et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Huggins C., Hodges C.V. Studies on prostatic cancer. I. The effect of castration, of estrogen and androgen injection on serum phosphatases in metastatic carcinoma of the prostate. CA Cancer J Clin. 1972;22(4):232–240. - PubMed
-
- Chen C.D., et al. Molecular determinants of resistance to antiandrogen therapy. Nat Med. 2004;10(1):33–39. - PubMed
-
- Scher H.I., et al. Increased survival with enzalutamide in prostate cancer after chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(13):1187–1197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

