The relationship between oxidative balance score and erectile dysfunction in the U.S. male adult population
- PMID: 38730004
- PMCID: PMC11087471
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-61287-w
The relationship between oxidative balance score and erectile dysfunction in the U.S. male adult population
Abstract
Oxidative stress strongly influences the pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction (ED). In this study, we used the oxidative balance score (OBS), a composite index, to measure the effects of oxidative stress triggered by diet and lifestyle factors. Here, we conducted a cross-sectional study to determine the statistical relationship between OBS and ED among adult males in the U.S. The data from 3318 participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001-2004 were analyzed. Weighted logistic regression was used to correct for confounding factors and acquire nationwide representative estimates. Generalized additive modeling was used to explore the nonlinear relationship. We also supplemented subgroup and sensitivity analysis to examine the robustness of the main results. Multivariate logistic regression indicated a consistent negative linear association between OBS and ED across all participants [OR (95% CI) = 0.96 (0.94, 0.98)]. After categorizing OBS into tertiles, participants in the highest tertile had 43% lower odds of having ED than those in the lowest tertile [OR (95% CI) = 0.57 (0.37, 0.87)]. The generalized additive model also visualized the linear trend of this association. Furthermore, this linear relationship remained relatively consistent, regardless of whether subgroup or sensitivity analyses were performed. Our findings suggest that adopting a lifestyle and diet pattern that promotes favorable OBS may effectively protect against the development of ED, regardless of the underlying causes.
Keywords: Cross-sectional study; Erectile dysfunction; Oxidative balance score; Oxidative stress.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
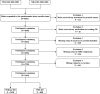
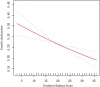

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- No.20223357025/Shenzhen Second People's Hospital Clinical Research Fund of Shenzhen High-level Hospital Construction Project
- 2022A1515011353/the National Science Foundation Projects of Guangdong Province, China
- SZSM20211100/Shenzhen "Medical and Health Sanming Project"
- SZXK020/Shenzhen Medical Key Discipline Construction Funds
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

