A tree-based corpus annotated with Cyber-Syndrome, symptoms, and acupoints
- PMID: 38730023
- PMCID: PMC11087536
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-024-03321-0
A tree-based corpus annotated with Cyber-Syndrome, symptoms, and acupoints
Abstract
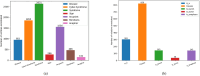
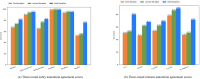
Prolonged and over-excessive interaction with cyberspace poses a threat to people's health and leads to the occurrence of Cyber-Syndrome, which covers not only physiological but also psychological disorders. This paper aims to create a tree-shaped gold-standard corpus that annotates the Cyber-Syndrome, clinical manifestations, and acupoints that can alleviate their symptoms or signs, designating this corpus as CS-A. In the CS-A corpus, this paper defines six entities and relations subject to annotation. There are 448 texts to annotate in total manually. After three rounds of updating the annotation guidelines, the inter-annotator agreement (IAA) improved significantly, resulting in a higher IAA score of 86.05%. The purpose of constructing CS-A corpus is to increase the popularity of Cyber-Syndrome and draw attention to its subtle impact on people's health. Meanwhile, annotated corpus promotes the development of natural language processing technology. Some model experiments can be implemented based on this corpus, such as optimizing and improving models for discontinuous entity recognition, nested entity recognition, etc. The CS-A corpus has been uploaded to figshare.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Ning H, Ye X, Bouras MA, Wei D, Daneshmand M. General cyberspace: Cyberspace and cyber-enabled spaces. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. 2018;5:1843–1856. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2815535. - DOI
-
- Ning H, Dhelim S, Bouras MA, Khelloufi A, Ullah A. Cyber-syndrome and its formation, classification, recovery and prevention. IEEE Access. 2018;6:35501–35511. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2848286. - DOI
-
- Kang Y, Cai Z, Tan CW, Huang Q, Liu H. Natural language processing(nlp)in management research:a literature review. Journal of Management Analytics. 2020;7:139–172. doi: 10.1080/23270012.2020.1756939. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

