m1A inhibition fuels oncolytic virus-elicited antitumor immunity via downregulating MYC/PD-L1 signaling
- PMID: 38730256
- PMCID: PMC11087574
- DOI: 10.1038/s41368-024-00304-0
m1A inhibition fuels oncolytic virus-elicited antitumor immunity via downregulating MYC/PD-L1 signaling
Abstract
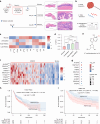
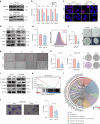
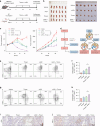
N1-methyladenosine (m1A) RNA methylation is critical for regulating mRNA translation; however, its role in the development, progression, and immunotherapy response of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) remains largely unknown. Using Tgfbr1 and Pten conditional knockout (2cKO) mice, we found the neoplastic transformation of oral mucosa was accompanied by increased m1A modification levels. Analysis of m1A-associated genes identified TRMT61A as a key m1A writer linked to cancer progression and poor prognosis. Mechanistically, TRMT61A-mediated tRNA-m1A modification promotes MYC protein synthesis, upregulating programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression. Moreover, m1A modification levels were also elevated in tumors treated with oncolytic herpes simplex virus (oHSV), contributing to reactive PD-L1 upregulation. Therapeutic m1A inhibition sustained oHSV-induced antitumor immunity and reduced tumor growth, representing a promising strategy to alleviate resistance. These findings indicate that m1A inhibition can prevent immune escape after oHSV therapy by reducing PD-L1 expression, providing a mutually reinforcing combination immunotherapy approach.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

