SLC34A2 Targets in Calcium/Phosphorus Homeostasis of Mammary Gland and Involvement in Development of Clinical Mastitis in Dairy Cows
- PMID: 38731279
- PMCID: PMC11083581
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14091275
SLC34A2 Targets in Calcium/Phosphorus Homeostasis of Mammary Gland and Involvement in Development of Clinical Mastitis in Dairy Cows
Abstract
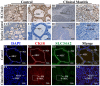
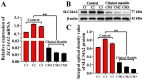
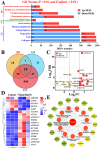
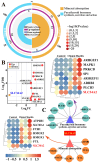
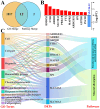
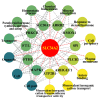
The type II Na/Pi co-transporter (NaPi2b), encoded by the solute carrier (SLC) transporter 34A2 (SLC34A2), is responsible for calcium (Ca) and phosphorus (P) homeostasis. Unbalanced Ca/P metabolism induces mastitis in dairy cows. However, the specific role of SLC34A2 in regulating this imbalance in Holstein cows with clinical mastitis (CM) remains unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of SLC34A2 and identify differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) that interact with SLC34A2 and are associated with Ca/P metabolism in dairy cows with CM. Immunohistochemical and immunofluorescence staining results showed that SLC34A2 was located primarily in the mammary epithelial cells of the mammary alveoli in both the control (healthy cows, Con/C) and CM groups. Compared to the Con/C group, the relative expression of the SLC34A2 gene and protein were significantly downregulated in the CM group. We identified 12 important DEPs included in 11 GO terms and two pathways interacting with SLC34A2 using data-independent acquisition proteomics. The PPI (protein-and-protein interaction) network results suggested that these DEPs were associated with ion metabolism and homeostasis, especially SLC34A2. These results demonstrate that SLC34A2 downregulation is negatively correlated with the occurrence and development of CM in Holstein cows, providing a basis for exploring the function and regulatory mechanism of SLC34A2 in Ca/P metabolism and homeostasis in Holstein cows with CM.
Keywords: SLC34A2; calcium/phosphorus homeostasis; mastitis; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang Q., Bai X., Shi J., Wang X., Zhang B., Dai L., Lin T., Gao Y., Zhang Y., Zhao X. DIA proteomics identified the potential targets associated with angiogenesis in the mammary glands of dairy cows with hemorrhagic mastitis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022;9:980963. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.980963. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vötterl J.C., Klinsoda J., Zebeli Q., Hennig-Pauka I., Kandler W., Metzler-Zebeli B.U. Dietary phytase and lactic acid-treated cereal grains differently affected calcium and phosphorus homeostasis from intestinal uptake to systemic metabolism in a pig model. Nutrients. 2020;12:1542. doi: 10.3390/nu12051542. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

