Analysis of the Immunogenicity of African Swine Fever F317L Protein and Screening of T Cell Epitopes
- PMID: 38731330
- PMCID: PMC11083013
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14091331
Analysis of the Immunogenicity of African Swine Fever F317L Protein and Screening of T Cell Epitopes
Abstract
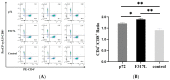
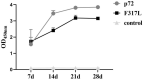
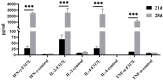
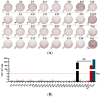
The African swine fever virus (ASFV) encodes numerous proteins characterized by complex immune escape mechanisms. At present, the structure and function of these proteins, including the F317L protein, have yet to be fully elucidated. In this study, we examined the immunogenicity of the F317L protein. Mice were subcutaneously immunized with the F317L protein using initial and subsequent booster doses, and, at the 28th day post-treatment, we assessed the humoral and cellular immune responses of mice. The F317L protein stimulated production of specific antibodies and activated humoral immune responses. In addition, F317L stimulated the production of large amounts of IFN-γ by splenic lymphocytes, thereby activating cellular immune responses. Using informatics technology, we predicted and synthesized 29 F317L protein T cell epitopes, which were screened using IFN-γ ELISpot. Among these, the F25 (246SRRSLVNPWT255) peptide was identified as having a stronger stimulatory effect than the full-length protein. Collectively, our findings revealed that the ASFV F317L protein can stimulate both strong humoral and cellular immunity in mice, and that the F25 (246SRRSLVNPWT255) peptide may be a potential active T cell epitope. These findings will provide a reference for further in-depth studies of the F317L protein and screening of antigenic epitopes.
Keywords: African swine fever virus; F317L protein; T cell epitope; cellular immunity; humoral immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
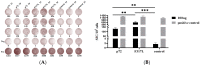
Similar articles
-
African Swine Fever Virus F317L Protein Inhibits NF-κB Activation To Evade Host Immune Response and Promote Viral Replication.mSphere. 2021 Oct 27;6(5):e0065821. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00658-21. Epub 2021 Oct 20. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34668754 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity Analysis and Identification of Potential T-Cell Epitopes in C129R Protein of African Swine Fever Virus.Microorganisms. 2024 May 24;12(6):1056. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061056. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930438 Free PMC article.
-
Thermostable T Cell Multiepitope Nanoparticle Antigens Inducing Potent Immune Responses against the Swine Fever Virus.ACS Infect Dis. 2023 Nov 10;9(11):2358-2368. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00506. Epub 2023 Oct 20. ACS Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37861250
-
Mucosal and cellular immune responses elicited by nasal and intramuscular inoculation with ASFV candidate immunogens.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 1;14:1200297. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1200297. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37720232 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and utility of innate immune system evasion mechanisms of ASFV.Virus Res. 2013 Apr;173(1):87-100. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2012.10.013. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Virus Res. 2013. PMID: 23165138 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and Biological Characteristics Study of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus GZ2022 Strain.Vet Sci. 2025 Jul 8;12(7):651. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12070651. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40711311 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of immunoprotective effects of PlpE multi-epitope protein incorporated within the aluminum hydroxide-adjuvanted inactivated vaccine against Pasteurella multocida infection in chickens.Poult Sci. 2025 Jun 14;104(9):105426. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105426. Online ahead of print. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40561824 Free PMC article.
-
Advancement in the Antigenic Epitopes and Vaccine Adjuvants of African Swine Fever Virus.Pathogens. 2024 Aug 21;13(8):706. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13080706. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39204306 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pietschmann J., Guinat C., Beer M., Pronin V., Tauscher K., Petrov A., Keil G., Blome S. Course and transmission characteristics of oral low-dose infection of domestic pigs and European wild boar with a Caucasian African swine fever virus isolate. Arch. Virol. 2015;160:1657–1667. doi: 10.1007/s00705-015-2430-2. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

