Gallic Acid Can Promote Low-Density Lipoprotein Uptake in HepG2 Cells via Increasing Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor Accumulation
- PMID: 38731489
- PMCID: PMC11085419
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29091999
Gallic Acid Can Promote Low-Density Lipoprotein Uptake in HepG2 Cells via Increasing Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor Accumulation
Abstract
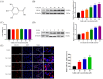
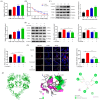
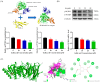
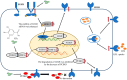
Gallic acid (GA) is a type of polyphenolic compound that can be found in a range of fruits, vegetables, and tea. Although it has been confirmed it improves non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), it is still unknown whether GA can improve the occurrence of NAFLD by increasing the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) accumulation and alleviating cholesterol metabolism disorders. Therefore, the present study explored the effect of GA on LDLR and its mechanism of action. The findings indicated that the increase in LDLR accumulation in HepG2 cells induced by GA was associated with the stimulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor-extracellular regulated protein kinase (EGFR-ERK1/2) signaling pathway. When the pathway was inhibited by EGFR mab cetuximab, it was observed that the activation of the EGFR-ERK1/2 signaling pathway induced by GA was also blocked. At the same time, the accumulation of LDLR protein and the uptake of LDL were also suppressed. Additionally, GA can also promote the accumulation of forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) and suppress the accumulation of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1α (HNF1α), leading to the inhibition of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9 (PCSK9) mRNA expression and protein accumulation. This ultimately results in increased LDLR protein accumulation and enhanced uptake of LDL in cells. In summary, the present study revealed the potential mechanism of GA's role in ameliorating NAFLD, with a view of providing a theoretical basis for the dietary supplementation of GA.
Keywords: LDLR; NAFLD; PCSK9; cholesterol metabolism; gallic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- He Y., Rodrigues R.M., Wang X., Seo W., Ma J., Hwang S., Fu Y., Trojnar E., Matyas C., Zhao S., et al. Neutrophil-to-hepatocyte communication via LDLR-dependent miR-223-enriched extracellular vesicle transfer ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2021;131:e141513. doi: 10.1172/JCI141513. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pouwels S., Sakran N., Graham Y., Leal A., Pintar T., Yang W., Kassir R., Singhal R., Mahawar K., Ramnarain D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022;22:63. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-00980-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Y.H., Hou J. Research progress in the regulation of cholesterol metabolism and its involvement in the occurrence and development of liver cancer. Chin. J. Cancer Biother. 2021;28:1215–1218.
-
- Zhang Q., Xu C., Tang Z.K. Regulation Mechanism of Intracellular Cholesterol Level. Prog. Biochem. BioPhys. 2022;49:292–302.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

