Structural Characterization of Polygonatum Cyrtonema Polysaccharide and Its Immunomodulatory Effects on Macrophages
- PMID: 38731567
- PMCID: PMC11085417
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29092076
Structural Characterization of Polygonatum Cyrtonema Polysaccharide and Its Immunomodulatory Effects on Macrophages
Abstract
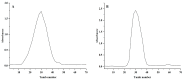
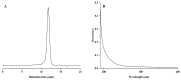
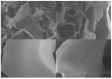
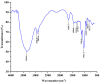
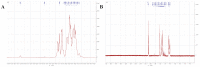
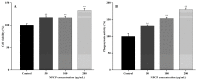
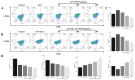
A neutral Polygonatum cyrtonema polysaccharide (NPCP) was isolated and purified from Polygonatum cyrtonema by various chromatographic techniques, including DEAE-52 and Sephadex-G100 chromatography. The structure of NPCP was characterized by HPLC, HPGPC, GC-MS, FT-IR, NMR, and SEM. Results showed that NPCP is composed of glucose (55.4%) and galactose (44.6%) with a molecular weight of 3.2 kDa, and the sugar chain of NPCP was →1)-α-D-Glc-(4→1)-β-D-Gal-(3→. In vitro bioactivity experiments demonstrated that NPCP significantly enhanced macrophages proliferation and phagocytosis while inhibiting the M1 polarization induced by LPS as well as the M2 polarization induced by IL-4 and IL-13 in macrophages. Additionally, NPCP suppressed the secretion of IL-6 and TNF-α in both M1 and M2 cells but promoted the secretion of IL-10. These results suggest that NPCP could serve as an immunomodulatory agent with potential applications in anti-inflammatory therapy.
Keywords: Polygonatum cyrtonema; immunomodulatory activity; polysaccharide; structure characterization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

