Stress Granule Core Protein-Derived Peptides Inhibit Assembly of Stress Granules and Improve Sorafenib Sensitivity in Cancer Cells
- PMID: 38731625
- PMCID: PMC11085366
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29092134
Stress Granule Core Protein-Derived Peptides Inhibit Assembly of Stress Granules and Improve Sorafenib Sensitivity in Cancer Cells
Abstract
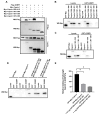
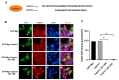
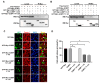
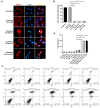
Upon a variety of environmental stresses, eukaryotic cells usually recruit translational stalled mRNAs and RNA-binding proteins to form cytoplasmic condensates known as stress granules (SGs), which minimize stress-induced damage and promote stress adaptation and cell survival. SGs are hijacked by cancer cells to promote cell survival and are consequently involved in the development of anticancer drug resistance. However, the design and application of chemical compounds targeting SGs to improve anticancer drug efficacy have rarely been studied. Here, we developed two types of SG inhibitory peptides (SIPs) derived from SG core proteins Caprin1 and USP10 and fused with cell-penetrating peptides to generate TAT-SIP-C1/2 and SIP-U1-Antp, respectively. We obtained 11 SG-inducing anticancer compounds from cell-based screens and explored the potential application of SIPs in overcoming resistance to the SG-inducing anticancer drug sorafenib. We found that SIPs increased the sensitivity of HeLa cells to sorafenib via the disruption of SGs. Therefore, anticancer drugs which are competent to induce SGs could be combined with SIPs to sensitize cancer cells, which might provide a novel therapeutic strategy to alleviate anticancer drug resistance.
Keywords: Caprin1; G3BP1; USP10; anticancer drug resistance; sorafenib; stress granules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
G3BP-Caprin1-USP10 complexes mediate stress granule condensation and associate with 40S subunits.J Cell Biol. 2016 Mar 28;212(7):845-60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201508028. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27022092 Free PMC article.
-
Psammaplysin F increases the efficacy of bortezomib and sorafenib through regulation of stress granule formation.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019 Jul;112:24-38. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.04.008. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31022461
-
Stress granule homeostasis is modulated by TRIM21-mediated ubiquitination of G3BP1 and autophagy-dependent elimination of stress granules.Autophagy. 2023 Jul;19(7):1934-1951. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2164427. Epub 2023 Jan 24. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 36692217 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting stress granules: A novel therapeutic strategy for human diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Nov;161:105143. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105143. Epub 2020 Aug 16. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32814168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the Ubiquitin System in Stress Granule Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 26;23(7):3624. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073624. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cholesterol-activated stress granules reduce the membrane localization of DRD2 and promote prolactinoma dopamine agonists resistance.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025 Apr 25;13(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s40478-025-01986-1. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025. PMID: 40281543 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

