Exploring the Efficiency of Algerian Kaolinite Clay in the Adsorption of Cr(III) from Aqueous Solutions: Experimental and Computational Insights
- PMID: 38731626
- PMCID: PMC11085289
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29092135
Exploring the Efficiency of Algerian Kaolinite Clay in the Adsorption of Cr(III) from Aqueous Solutions: Experimental and Computational Insights
Abstract
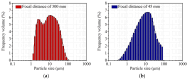
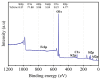
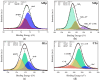
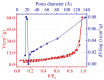
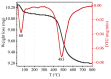
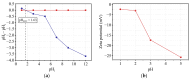
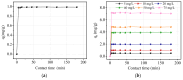
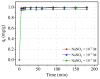
The current study comprehensively investigates the adsorption behavior of chromium (Cr(III)) in wastewater using Algerian kaolinite clay. The structural and textural properties of the kaolinite clay are extensively characterized through a range of analytical methods, including XRD, FTIR, SEM-EDS, XPS, laser granulometry, N2 adsorption isotherm, and TGA-DTA. The point of zero charge and zeta potential are also assessed. Chromium adsorption reached equilibrium within five minutes, achieving a maximum removal rate of 99% at pH 5. Adsorption equilibrium is modeled using the Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin, Elovich, and Dubinin-Radushkevitch equations, with the Langmuir isotherm accurately describing the adsorption process and yielding a maximum adsorption capacity of 8.422 mg/g for Cr(III). Thermodynamic parameters suggest the spontaneous and endothermic nature of Cr(III) sorption, with an activation energy of 26.665 kJ/mol, indicating the importance of diffusion in the sorption process. Furthermore, advanced DFT computations, including COSMO-RS, molecular orbitals, IGM, RDG, and QTAIM analyses, are conducted to elucidate the nature of adsorption, revealing strong binding interactions between Cr(III) ions and the kaolinite surface. The integration of theoretical and experimental data not only enhances the understanding of Cr(III) removal using kaolinite but also demonstrates the effectiveness of this clay adsorbent for wastewater treatment. Furthermore, this study highlights the synergistic application of empirical research and computational modeling in elucidating complex adsorption processes.
Keywords: COSMO-RS; DFT; adsorption; chromium; kaolinite; quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Uptake of trivalent chromium ions from aqueous solutions using kaolinite.J Hazard Mater. 2007 Sep 5;148(1-2):56-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.02.007. Epub 2007 Feb 12. J Hazard Mater. 2007. PMID: 17363144
-
The role of bentonite clay and bentonite clay@MnFe2O4 composite and their physico-chemical properties on the removal of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) from aqueous media.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Apr;27(12):14044-14057. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-07756-x. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32036528
-
Adsorption of polyvinylimidazole onto kaolinite.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2006 Apr 15;296(2):472-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2005.09.049. Epub 2005 Nov 18. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2006. PMID: 16298380
-
Adsorption properties of kaolinite-based nanocomposites for Fe and Mn pollutants from aqueous solutions and raw ground water: kinetics and equilibrium studies.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Oct;24(29):22954-22966. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9942-0. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28819905
-
RSM optimization studies for cadmium ions adsorption onto pristine and acid-modified kaolinite clay.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 27;9(8):e18634. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18634. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37554808 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Adsorption of Bichromate and Arsenate Anions by a Sorbent Based on Bentonite Clay Modified with Polyhydroxocations of Iron and Aluminum by the "Co-Precipitation" Method.Molecules. 2024 Aug 5;29(15):3709. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153709. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39125112 Free PMC article.
-
The application of Rumex Abysinicus derived activated carbon/bentonite clay/graphene oxide/iron oxide nanocomposite for removal of chromium from aqueous solution.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 20;14(1):19280. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70238-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39164377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbou B., Lebkiri I., Ouaddari H., Elkhattabi O., Habsaoui A., Lebkiri A., El Housseine R. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Study on Adsorption of Cadmium from Aqueous Solutions Using Natural Clay. J. Turk. Chem. Soc. Sect. A Chem. 2021;8:677–692. doi: 10.18596/jotcsa.882016. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

