Purification and Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Culture Supernatant of Coprinus comatus
- PMID: 38731663
- PMCID: PMC11083162
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13091292
Purification and Biochemical Characterization of a Novel Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Culture Supernatant of Coprinus comatus
Abstract
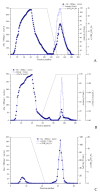
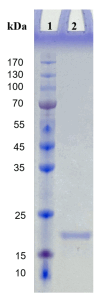
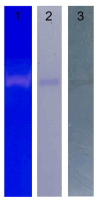
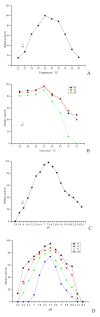
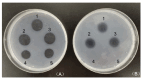
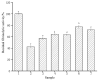
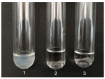
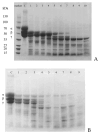
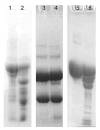
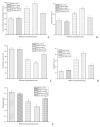
A novel fibrinolytic enzyme was produced by the liquid fermentation of Coprinus comatus. The enzyme was purified from the culture supernatant by hydrophobic interactions, gel filtration, and ion exchange chromatographies. It was purified by 241.02-fold, with a specific activity of 3619 U/mg and a final yield of 10.02%. SDS-PAGE analysis confirmed the purity of the enzyme, showing a single band with a molecular weight of 19.5 kDa. The first nine amino acids of the N-terminal of the purified enzyme were A-T-Y-T-G-G-S-Q-T. The enzyme exhibited optimal activity at a temperature of 42 °C and pH 7.6. Its activity was significantly improved by Zn2+, K+, Ca2+, Mn2+, and Mg2+ while being inhibited by Fe2+, Fe3+, Al2+, and Ba2+. The activity of the enzyme was completely inhibited by ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA), and it was also dose-dependently inhibited by phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) and soy trypsin inhibitor (SBTI). However, inhibitors such as N-α-tosyl-L-phenylalanine chloromethyl ketone (TPCK), aprotinin, and pepstatin did not significantly affect its activity, suggesting that the enzyme was a serine-like metalloproteinase. The enzyme acted as both a plasmin-like fibrinolytic enzyme and a plasminogen activator, and it also exhibited the capability to hydrolyze fibrinogen and fibrin. In vitro, it demonstrated the ability to dissolve blood clots and exhibit anticoagulant properties. Furthermore, it was found that the enzyme prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), prothrombin time (PT), and thrombin time (TT), and reduced the levels of fibrinogen (FIB) and prothrombin activity (PA). Based on these studies, the enzyme has great potential to be developed as a natural agent for the prevention and treatment of thrombotic diseases.
Keywords: Coprinus comatus; anticoagulant activity; fermentation; fibrinolytic enzyme.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Parveen A., Devika R. Fibrinolytic Enzyme—An Overview. Curr. Pharm. Biotechno. 2022;23:1336–1345. - PubMed
-
- Yao M.J., Yang Y., Fan J., Ma C., Liu X.F., Wang Y., Wang B., Sun Z.H., McClements D.J., Zhang J.X., et al. Production, purification, and functional properties of microbial fibrinolytic enzymes produced by microorganism obtained from soy-based fermented foods: Developments and challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2022:2134980. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2134980. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kumar S.S., Sabu A. Fibrinolytic Enzymes for Thrombolytic Therapy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019;1148:345–381. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- ZY23QY06/The central government guides local science and technology development projects
- 31171744/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- ZD201305/Heilongjiang Province Natural Science Foundation key project
- 52270074/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 145209314/Heilongjiang Province basic scientific research operating expenses scientific research projects
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

