Contemporary Views of the Extraction, Health Benefits, and Industrial Integration of Rice Bran Oil: A Prominent Ingredient for Holistic Human Health
- PMID: 38731675
- PMCID: PMC11083700
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13091305
Contemporary Views of the Extraction, Health Benefits, and Industrial Integration of Rice Bran Oil: A Prominent Ingredient for Holistic Human Health
Abstract
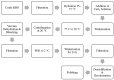
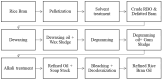
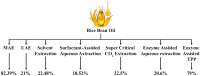
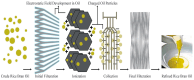
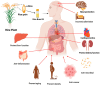
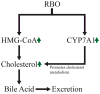
Globally, 50% of people consume rice (Oryza sativa), which is among the most abundant and extensively ingested cereal grains. Rice bran is a by-product of the cereal industry and is also considered a beneficial waste product of the rice processing industry. Rice bran oil (RBO) is created from rice bran (20-25 wt% in rice bran), which is the outermost layer of the rice kernel; has a lipid content of up to 25%; and is a considerable source of a plethora of bioactive components. The main components of RBO include high levels of fiber and phytochemicals, including vitamins, oryzanols, fatty acids, and phenolic compounds, which are beneficial to human health and well-being. This article summarizes the stabilization and extraction processes of rice bran oil from rice bran using different techniques (including solvent extraction, microwaving, ohmic heating, supercritical fluid extraction, and ultrasonication). Some studies have elaborated the various biological activities linked with RBO, such as antioxidant, anti-platelet, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-thrombotic, anti-mutagenic, aphrodisiac, anti-depressant, anti-emetic, fibrinolytic, and cytotoxic activities. Due to the broad spectrum of biological activities and economic benefits of RBO, the current review article focuses on the extraction process of RBO, its bioactive components, and the potential health benefits of RBO. Furthermore, the limitations of existing studies are highlighted, and suggestions are provided for future applications of RBO as a functional food ingredient.
Keywords: bioactive components; cereal characterization; food industry; production and health benefits; rice by-product.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nutrients in rice bran oil and their nutritional functions: a review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025;65(14):2840-2857. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2024.2352530. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 38856105 Review.
-
Facile analysis of rice bran oil to compare free unsaturated fatty acid compositions of parental and hybrid rice lines.J Am Oil Chem Soc. 2022 Dec;99(12):1103-1111. doi: 10.1002/aocs.12631. Epub 2022 Aug 3. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 2022. PMID: 36589259 Free PMC article.
-
Rice Bran Stabilisation and Oil Extraction Using the Microwave-Assisted Method and Its Effects on GABA and Gamma-Oryzanol Compounds.Foods. 2022 Mar 22;11(7):912. doi: 10.3390/foods11070912. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35406999 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Extraction Methods on Phytochemicals of Rice Bran Oils Produced from Colored Rice.J Oleo Sci. 2018 Feb 1;67(2):135-142. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess17122. Epub 2018 Jan 23. J Oleo Sci. 2018. PMID: 29367480
-
Biological Functions and Activities of Rice Bran as a Functional Ingredient: A Review.Nutr Metab Insights. 2021 Dec 5;14:11786388211058559. doi: 10.1177/11786388211058559. eCollection 2021. Nutr Metab Insights. 2021. PMID: 34898989 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of triple-frequency sono-germination and soaking treatments on techno-functional characteristics of barley.Ultrason Sonochem. 2025 Feb;113:107231. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2025.107231. Epub 2025 Jan 12. Ultrason Sonochem. 2025. PMID: 39826486 Free PMC article.
-
Rice Bran Consumption Improves Lipid Profiles: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 30;17(1):114. doi: 10.3390/nu17010114. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39796546 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Phytonutrients in the Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases: A Concrete Review.ACS Omega. 2025 Mar 27;10(13):12724-12755. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c02927. eCollection 2025 Apr 8. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40224418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Thermal Stabilization Strategies for Rice Bran: Mechanistic Insights, Technological Advances, and Implications for Industrial Applications.Foods. 2025 Apr 22;14(9):1448. doi: 10.3390/foods14091448. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40361531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties of Goat Milk Enriched With Rice Extract Fermented by Exopolysaccharide-Producing Lactic Bacteria for Functional Yogurt Production.Int J Food Sci. 2025 Jun 5;2025:8008452. doi: 10.1155/ijfo/8008452. eCollection 2025. Int J Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40520528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nagendra Prasad M.N., Sanjay K.R., Shravya Khatokar M., Vismaya M.N., Nanjunda Swamy S. Health Benefits of Rice Bran—A Review. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2011;1:1000108. doi: 10.4172/2155-9600.1000108. - DOI
-
- Verma D.K., Srivastav P.P. Bioactive compounds of rice (Oryza sativa L.): Review on paradigm and its potential benefit in human health. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020;97:355–365. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.01.007. - DOI
-
- Zhang Y., Liu J., Yuan W., Zhang R., Xi X. Multiple leveling for paddy field preparation with double axis rotary tillage accelerates rice growth and economic benefits. Agriculture. 2021;11:1223. doi: 10.3390/agriculture11121223. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

