Steatotic Donor Transplant Livers: Preservation Strategies to Mitigate against Ischaemia-Reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 38731866
- PMCID: PMC11083584
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25094648
Steatotic Donor Transplant Livers: Preservation Strategies to Mitigate against Ischaemia-Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
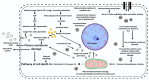
Liver transplantation (LT) is the only definitive treatment for end-stage liver disease, yet the UK has seen a 400% increase in liver disease-related deaths since 1970, constrained further by a critical shortage of donor organs. This shortfall has necessitated the use of extended criteria donor organs, including those with evidence of steatosis. The impact of hepatic steatosis (HS) on graft viability remains a concern, particularly for donor livers with moderate to severe steatosis which are highly sensitive to the process of ischaemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) and static cold storage (SCS) leading to poor post-transplantation outcomes. This review explores the pathophysiological predisposition of steatotic livers to IRI, the limitations of SCS, and alternative preservation strategies, including novel organ preservation solutions (OPS) and normothermic machine perfusion (NMP), to mitigate IRI and improve outcomes for steatotic donor livers. By addressing these challenges, the liver transplant community can enhance the utilisation of steatotic donor livers which is crucial in the context of the global obesity crisis and the growing need to expand the donor pool.
Keywords: defatting; ischaemia-free liver transplantation; normothermic machine perfusion; organ preservation solution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- NHS Digital Statistics on Obesity, Physical Activity and Diet: England 2015. 2015. [(accessed on 4 November 2019)]. Available online: https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/sta....
-
- NHS Blood and Transfusion (NHSBT) Annual Report on Liver Transplantation. 2019. [(accessed on 22 November 2019)]. Available online: https://nhsbtdbe.blob.core.windows.net/umbraco-assets-corp/16782/nhsbt-l....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

