Plasma Metabolite Profiling in the Search for Early-Stage Biomarkers for Lung Cancer: Some Important Breakthroughs
- PMID: 38731909
- PMCID: PMC11083579
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25094690
Plasma Metabolite Profiling in the Search for Early-Stage Biomarkers for Lung Cancer: Some Important Breakthroughs
Abstract
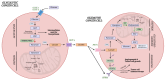
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. In order to improve its overall survival, early diagnosis is required. Since current screening methods still face some pitfalls, such as high false positive rates for low-dose computed tomography, researchers are still looking for early biomarkers to complement existing screening techniques in order to provide a safe, faster, and more accurate diagnosis. Biomarkers are biological molecules found in body fluids, such as plasma, that can be used to diagnose a condition or disease. Metabolomics has already been shown to be a powerful tool in the search for cancer biomarkers since cancer cells are characterized by impaired metabolism, resulting in an adapted plasma metabolite profile. The metabolite profile can be determined using nuclear magnetic resonance, or NMR. Although metabolomics and NMR metabolite profiling of blood plasma are still under investigation, there is already evidence for its potential for early-stage lung cancer diagnosis, therapy response, and follow-up monitoring. This review highlights some key breakthroughs in this research field, where the most significant biomarkers will be discussed in relation to their metabolic pathways and in light of the altered cancer metabolism.
Keywords: NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance); biomarkers; lung cancer; metabolomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Metabolic profiling of potential lung cancer biomarkers using bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and the integrated direct infusion/ gas chromatography mass spectrometry platform.J Proteomics. 2016 Aug 11;145:197-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.05.030. Epub 2016 May 30. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27255828
-
Unraveling the Rewired Metabolism in Lung Cancer Using Quantitative NMR Metabolomics.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 17;23(10):5602. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105602. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-targeted and targeted metabolomics approaches to diagnosing lung cancer and predicting patient prognosis.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 27;7(39):63437-63448. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11521. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27566571 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy as a new approach for improvement of early diagnosis and risk stratification of prostate cancer.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017 Nov.;18(11):921-933. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1600441. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2017. PMID: 29119730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum metabolomic profiling of prostate cancer risk in the prostate, lung, colorectal, and ovarian cancer screening trial.Br J Cancer. 2016 Oct 25;115(9):1087-1095. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.305. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Br J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27673363 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wood D.E., Kazerooni E.A., Baum S.L., Eapen G.A., Ettinger D.S., Hou L., Jackman D.M., Klippenstein D., Kumar R., Lackner R.P., et al. Lung Cancer Screening, Version 3.2018, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018;16:412–441. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

