Examination of the Complex Molecular Landscape in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 38732002
- PMCID: PMC11084226
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25094781
Examination of the Complex Molecular Landscape in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
The escalating prevalence of metabolic disorders, notably type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity, presents a critical global health challenge, necessitating deeper insights into their molecular underpinnings. Our study integrates proteomics and metabolomics analyses to delineate the complex molecular landscapes associated with T2D and obesity. Leveraging data from 130 subjects, including individuals with T2D and obesity as well as healthy controls, we elucidate distinct molecular signatures and identify novel biomarkers indicative of disease progression. Our comprehensive characterization of cardiometabolic proteins and serum metabolites unveils intricate networks of biomolecular interactions and highlights differential protein expression patterns between T2D and obesity cohorts. Pathway enrichment analyses reveal unique mechanisms underlying disease development and progression, while correlation analyses elucidate the interplay between proteomics, metabolomics, and clinical parameters. Furthermore, network analyses underscore the interconnectedness of cardiometabolic proteins and provide insights into their roles in disease pathogenesis. Our findings may help to refine diagnostic strategies and inform the development of personalized interventions, heralding a new era in precision medicine and healthcare innovation. Through the integration of multi-omics approaches and advanced analytics, our study offers a crucial framework for deciphering the intricate molecular underpinnings of metabolic disorders and paving the way for transformative therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: data integration; metabolomics; obesity; proteomics; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
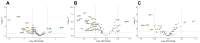


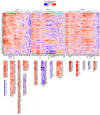
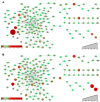
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

