Estrogen-Related Receptor α: A Key Transcription Factor in the Regulation of Energy Metabolism at an Organismic Level and a Target of the ABA/LANCL Hormone Receptor System
- PMID: 38732013
- PMCID: PMC11084903
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25094796
Estrogen-Related Receptor α: A Key Transcription Factor in the Regulation of Energy Metabolism at an Organismic Level and a Target of the ABA/LANCL Hormone Receptor System
Abstract
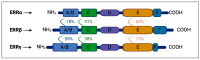
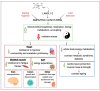
The orphan nuclear receptor ERRα is the most extensively researched member of the estrogen-related receptor family and holds a pivotal role in various functions associated with energy metabolism, especially in tissues characterized by high energy requirements, such as the heart, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, kidney, and brain. Abscisic acid (ABA), traditionally acknowledged as a plant stress hormone, is detected and actively functions in organisms beyond the land plant kingdom, encompassing cyanobacteria, fungi, algae, protozoan parasites, lower Metazoa, and mammals. Its ancient, cross-kingdom role enables ABA and its signaling pathway to regulate cell responses to environmental stimuli in various organisms, such as marine sponges, higher plants, and humans. Recent advancements in understanding the physiological function of ABA and its mammalian receptors in governing energy metabolism and mitochondrial function in myocytes, adipocytes, and neuronal cells suggest potential therapeutic applications for ABA in pre-diabetes, diabetes, and cardio-/neuroprotection. The ABA/LANCL1-2 hormone/receptor system emerges as a novel regulator of ERRα expression levels and transcriptional activity, mediated through the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α axis. There exists a reciprocal feed-forward transcriptional relationship between the LANCL proteins and transcriptional coactivators ERRα/PGC-1α, which may be leveraged using natural or synthetic LANCL agonists to enhance mitochondrial function across various clinical contexts.
Keywords: AMPK/PGC-1α/SIRT1; BAT; biogenesis and proton gradient; cardioprotection; energy production; kidney; mitochondrial function; neurodegeneration; oxidative stress; oxphos uncoupling; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Eudy J.D., Yao S., Weston M.D., Ma-Edmonds M., Talmadge C.B., Cheng J.J., Kimberling W.J., Sumegi J. Isolation of a gene encoding a novel member of the nuclear receptor superfamily from the critical region of Usher syndrome type IIa at 1q41. Genomics. 1998;50:382–384. doi: 10.1006/geno.1998.5345. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

