SGLT2 Inhibitors in Kidney Diseases-A Narrative Review
- PMID: 38732178
- PMCID: PMC11084583
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25094959
SGLT2 Inhibitors in Kidney Diseases-A Narrative Review
Abstract
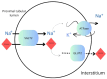
Some of the most common conditions affecting people are kidney diseases. Among them, we distinguish chronic kidney disease and acute kidney injury. Both entities pose serious health risks, so new drugs are still being sought to treat and prevent them. In recent years, such a role has begun to be assigned to sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. They increase the amount of glucose excreted in the urine. For this reason, they are currently used as a first-line drug in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Due to their demonstrated cardioprotective effect, they are also used in heart failure treatment. As for the renal effects of SGLT2 inhibitors, they reduce intraglomerular pressure and decrease albuminuria. This results in a slower decline in glomelular filtration rate (GFR) in patients with kidney disease. In addition, these drugs have anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects. In the following article, we review the evidence for the effectiveness of this group of drugs in kidney disease and their nephroprotective effect. Further research is still needed, but meta-analyses indicate SGLT2 inhibitors' efficacy in kidney disease, especially the one caused by diabetes. Development of new drugs and clinical trials on specific patient subgroups will further refine their nephroprotective effects.
Keywords: SGLT2 inhibitors; acute kidney injury; chronic kidney disease; nephroprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renal Protection with SGLT2 Inhibitors: Effects in Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease.Curr Diab Rep. 2022 Jan;22(1):39-52. doi: 10.1007/s11892-021-01442-z. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Curr Diab Rep. 2022. PMID: 35113333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Role for Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Mini Review.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2023;48(1):599-610. doi: 10.1159/000534174. Epub 2023 Sep 16. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2023. PMID: 37717569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal Effects of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter Inhibitors.Am J Cardiol. 2019 Dec 15;124 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S28-S35. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2019.10.027. Am J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31741437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SGLT2 Inhibitors and the Diabetic Kidney.Diabetes Care. 2016 Aug;39 Suppl 2:S165-71. doi: 10.2337/dcS15-3006. Diabetes Care. 2016. PMID: 27440829
-
Evaluation of renal and cardiovascular protection mechanisms of SGLT2 inhibitors: model-based analysis of clinical data.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):F1295-F1306. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00202.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30019930 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Incretins and SGLT-2 inhibitors in diabetic patients with neuroendocrine tumors: current updates and future directions.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2025 Aug;26(4):575-592. doi: 10.1007/s11154-025-09958-5. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2025. PMID: 40175622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In the Era of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome in Cardio-Oncology: From Pathogenesis to Prevention and Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Mar 30;17(7):1169. doi: 10.3390/cancers17071169. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors: Focus on Macrophages.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 15;26(4):1670. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041670. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-term effects of empagliflozin on preventing contrast induced acute kidney injury in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, a randomised trial.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 31;15(1):3940. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82991-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39890841 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Update on the Efficacy and Safety of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in Patients with Chronic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jan 23;61(2):202. doi: 10.3390/medicina61020202. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40005319 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

