Deciphering the Prognostic Efficacy of MRI Radiomics in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38732337
- PMCID: PMC11082984
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14090924
Deciphering the Prognostic Efficacy of MRI Radiomics in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis
Abstract
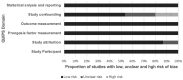
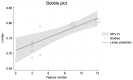
This meta-analysis investigates the prognostic value of MRI-based radiomics in nasopharyngeal carcinoma treatment outcomes, specifically focusing on overall survival (OS) variability. The study protocol was registered with INPLASY (INPLASY202420101). Initially, a systematic review identified 15 relevant studies involving 6243 patients through a comprehensive search across PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science, adhering to PRISMA guidelines. The methodological quality was assessed using the Quality in Prognosis Studies (QUIPS) tool and the Radiomics Quality Score (RQS), highlighting a low risk of bias in most domains. Our analysis revealed a significant average concordance index (c-index) of 72% across studies, indicating the potential of radiomics in clinical prognostication. However, moderate heterogeneity was observed, particularly in OS predictions. Subgroup analyses and meta-regression identified validation methods and radiomics software as significant heterogeneity moderators. Notably, the number of features in the prognosis model correlated positively with its performance. These findings suggest radiomics' promising role in enhancing cancer treatment strategies, though the observed heterogeneity and potential biases call for cautious interpretation and standardization in future research.
Keywords: meta-analysis; prognostic models; radiomics; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the prognostic value of 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) and/or computed tomography (CT)-based radiomics in head and neck cancer.Clin Radiol. 2024 Oct;79(10):757-772. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2024.05.016. Epub 2024 May 27. Clin Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38944542
-
A systematic review of radiomics in osteosarcoma: utilizing radiomics quality score as a tool promoting clinical translation.Eur Radiol. 2021 Mar;31(3):1526-1535. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07221-w. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 32876837
-
Radiomics for predicting survival in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Dec 1;13(12):8395-8412. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-692. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 38106286 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics diagnostic performance for predicting lymph node metastasis in esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Jun 12;24(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01278-5. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38867143 Free PMC article.
-
Quality assessment of the MRI-radiomics studies for MGMT promoter methylation prediction in glioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2024 Sep;34(9):5802-5815. doi: 10.1007/s00330-024-10594-x. Epub 2024 Feb 3. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38308012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lambin P., Rios-Velazquez E., Leijenaar R., Carvalho S., van Stiphout R.G.P.M., Granton P., Zegers C.M.L., Gillies R., Boellard R., Dekker A., et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer. 2012;48:441–446. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.036. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aerts H.J., Velazquez E.R., Leijenaar R.T., Parmar C., Grossmann P., Carvalho S., Bussink J., Monshouwer R., Haibe-Kains B., Rietveld D., et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:4006. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

