Modified RTK-GNSS for Challenging Environments
- PMID: 38732821
- PMCID: PMC11086102
- DOI: 10.3390/s24092712
Modified RTK-GNSS for Challenging Environments
Abstract
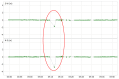
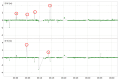
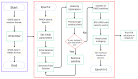
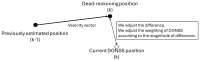
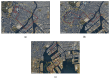
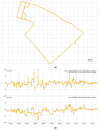
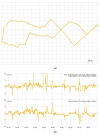
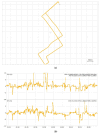
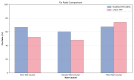
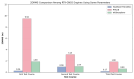
Real-Time Kinematic Global Navigation Satellite System (RTK-GNSS) is currently the premier technique for achieving centimeter-level accuracy quickly and easily. However, the robustness of RTK-GNSS diminishes in challenging environments due to severe multipath effects and a limited number of available GNSS signals. This is a pressing issue, especially for GNSS users in the navigation industry. This paper proposes and evaluates several methodologies designed to overcome these issues by enhancing the availability and reliability of RTK-GNSS solutions in urban environments. Our novel approach involves the integration of conventional methods with a new technique that leverages surplus satellites-those not initially used for positioning-to more reliably detect incorrect fix solutions. We conducted three tests in densely built-up areas within the Tokyo region. The results demonstrate that our approach not only surpasses the fix rate of the latest commercial receivers and a popular open-source RTK-GNSS program but also improves positional reliability to levels comparable to or exceeding those of the aforementioned commercial technology.
Keywords: RTK; multipath; navigation; reliability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Hegarty C., Kaplan E. Understanding GPS Principles and Applications. 2nd ed. Artech House; Boston, MA, USA: 2005. pp. 397–424.
-
- Walsh D. Real-Time Ambiguity Resolution While on the Move; Proceedings of the ION Satellite Division’s 5th International Meeting; Albuquerque, NM, USA. 16–18 September 1992; pp. 473–481.
-
- ESA Navipedia. [(accessed on 8 February 2024)]. Available online: https://gssc.esa.int/navipedia/
-
- Takasu T., Yasuda A. Development of the low-cost RTK-GPS receiver with an open source program package RTKLIB. Development, Evaluation, and Application of RTKLIB: A Program Library for RTK-GPS; Proceedings of the International Symposium on GPS/GNSS; International Conventional Center, Jeju, Republic of Korea. 4 November 2009; pp. 1–6.
-
- Wen W., Hsu L.T. Towards Robust GNSS Positioning and Real-time Kinematic Using Factor Graph Optimization; Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA); Xi’an, China. 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 5884–5890. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

