Long-term use of interleukin-1 inhibitors reduce flare activity in patients with fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva
- PMID: 38733591
- PMCID: PMC11371373
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae255
Long-term use of interleukin-1 inhibitors reduce flare activity in patients with fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva
Abstract
Objectives: Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) is one of the most catastrophic forms of genetic heterotopic ossification (HO). FOP is characterized by severe, progressive inflammatory flare-ups, that often lead to HO. The flare-ups are associated with increased inflammatory cytokine production, suggesting auto-inflammatory features driven by IL-1β. This study describes the short- and long-term responses of FOP patients to anti-IL-1 therapy.
Methods: Previously, we reported that a patient with FOP treated with anti-IL-1 agents showed dramatically lower rates of flare-ups, improved flare-up symptoms, decreased use of glucocorticoids and apparently decreased size of residual lesions. Plasma analyses also showed marked elevation in IL-1β levels during a FOP flare, further supporting a role of IL-1β in the pathogenesis of FOP flares. Here, we report results from long-term therapy with IL-1 inhibitors in that patient and describe 3 additional patients, from two medical centres.
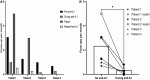
Results: All 4 patients showed persistent improvement in flare activity during treatment with IL-1 inhibitors, with minimal formation of new HO sites. Two patients who stopped therapy experienced a resurgence of flare activity that was re-suppressed upon re-initiation. These patients had IL-1β levels comparable to those in IL-1β-driven diseases. Child Health Assessment Questionnaires confirmed extensive subjective improvements in the pain and general health visual analogue scales.
Conclusion: This case series demonstrates significant benefits from IL-1 inhibitors for reducing flare activity and improving the general health of patients with FOP. These data provide strong support for additional studies to better understand the function of IL-1 inhibition, primarily in reducing the formation of new HO.
Funding: RH received support from the International FOP Association ACT grant; ECH received support from NIH/NIAMS R01AR073015 and the UCSF Robert Kroc Chair in Connective Tissue and Rheumatic Diseases III.
Keywords: IL-1; IL-1β; anakinra; canakinumab; fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva; heterotopic ossification; interleukin.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures


References
-
- Kaplan FS, Al Mukaddam M, Baujat G. et al.; The International Clinical Council on FOP. The medical management of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: current treatment considerations . Proc Intl Clin Council FOP 2021;2:1–128.
-
- Bauer AH, Bonham J, Gutierrez L, Hsiao EC, Motamedi D.. Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: a current review of imaging findings. Skeletal Radiol 2018;47:1043–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

