Unusual phenotype in 35delG mutation: a case report
- PMID: 38734626
- PMCID: PMC11088767
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-024-04559-3
Unusual phenotype in 35delG mutation: a case report
Abstract
Background: Mutations in the GJB2 gene, which encodes the protein connexin 26 and is involved in inner ear homeostasis, are identified in approximately 50% of patients with autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss, making it one of the primary causes of prelingual nonsyndromic hearing loss in various populations. The 35delG mutation, one of the most common mutations of the GJB2 gene, usually causes prelingual, bilateral mild to profound, nonprogressive sensorineural hearing loss.
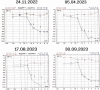
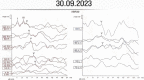
Case presentation: We present an unusual case of an 18-year-old Turkish female with heterozygous 35delG mutation and postlingual, profound-sloping, progressive and fluctuating unilateral sensorineural hearing loss. The phenotype is different from the usual findings.
Conclusions: The 35delG mutation causing hearing loss may not always be reflected in the phenotype as expected and therefore may have different audiologic manifestations.
Keywords: 35delG mutation; GJB2; Genetic hearing loss; Unilateral progressive hearing loss.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Frequency of the Connexin26/35delG mutation and its characteristic phenotype in patients with hearing impairment and controls in Northeastern Hungary].Orv Hetil. 2002 Oct 6;143(40):2285-9. Orv Hetil. 2002. PMID: 12420583 Hungarian.
-
Frequency of GJB2 mutations in patients with nonsyndromic hearing loss from an ethnically characterized Brazilian population.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Jan-Feb;85(1):92-98. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2017.10.013. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 29773520 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate hearing loss and pseudodominant inheritance due to L90P/35delG mutations in the GJB2 (connexin 26) gene.Genet Couns. 2003;14(4):379-86. Genet Couns. 2003. PMID: 14738110 Review.
-
Clinical studies of families with hearing loss attributable to mutations in the connexin 26 gene (GJB2/DFNB1).Pediatrics. 1999 Mar;103(3):546-50. doi: 10.1542/peds.103.3.546. Pediatrics. 1999. PMID: 10049954
-
Clinical phenotype and mutations in connexin 26 (DFNB1/GJB2), the most common cause of childhood hearing loss.Am J Med Genet. 1999 Sep 24;89(3):130-6. Am J Med Genet. 1999. PMID: 10704187 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources