Elevated SCN11A concentrations associated with lower serum lipid levels in patients with major depressive disorder
- PMID: 38734669
- PMCID: PMC11088647
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-024-02916-w
Elevated SCN11A concentrations associated with lower serum lipid levels in patients with major depressive disorder
Abstract
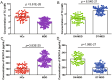
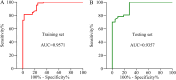
The pathogenesis of major depressive disorder (MDD) involves lipid metabolism. Our earlier research also revealed that MDD patients had much lower total cholesterol (TC) concentrations than healthy controls (HCs). However, it is still unclear why TC decreased in MDD. Here, based on the Ingenuity Knowledge Base's ingenuity pathway analysis, we found that sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 11A (SCN11A) might serve as a link between low lipid levels and MDD. We analyzed the TC levels and used ELISA kits to measure the levels of SCN11A in the serum from 139 MDD patients, and 65 HCs to confirm this theory and explore the potential involvement of SCN11A in MDD. The findings revealed that TC levels were considerably lower and SCN11A levels were remarkably increased in MDD patients than those in HCs, while they were significantly reversed in drug-treatment MDD patients than in drug-naïve MDD patients. There was no significant difference in SCN11A levels among MDD patients who used single or multiple antidepressants, and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or other antidepressants. Pearson correlation analysis showed that the levels of TC and SCN11A were linked with the Hamilton Depression Rating Scales score. A substantial association was also found between TC and SCN11A. Moreover, a discriminative model made up of SCN11A was discovered, which produced an area under a curve of 0.9571 in the training set and 0.9357 in the testing set. Taken together, our findings indicated that SCN11A may serve as a link between low lipid levels and MDD, and showed promise as a candidate biomarker for MDD.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MANF/EWSR1/ANXA6 pathway might as the bridge between hypolipidemia and major depressive disorder.Transl Psychiatry. 2022 Dec 30;12(1):527. doi: 10.1038/s41398-022-02287-0. Transl Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36585419 Free PMC article.
-
LRFN5 and OLFM4 as novel potential biomarkers for major depressive disorder: a pilot study.Transl Psychiatry. 2023 Jun 6;13(1):188. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02490-7. Transl Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37280213 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced serum BDNF levels are associated with the increased risk for developing MDD: a case-control study with or without antidepressant therapy.BMC Res Notes. 2020 Feb 21;13(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13104-020-04952-3. BMC Res Notes. 2020. PMID: 32085720 Free PMC article.
-
Altered γ-aminobutyric acid neurotransmission in major depressive disorder: a critical review of the supporting evidence and the influence of serotonergic antidepressants.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jan 19;9:603-24. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S62912. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25653499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 5-HT1B receptor - a potential target for antidepressant treatment.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 May;235(5):1317-1334. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4872-1. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018. PMID: 29546551 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the modulatory effects of lactoferrin on depressed rats through 16S rDNA gene sequencing and LC-MS metabolomics analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 27;14(1):22111. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72793-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39333605 Free PMC article.
-
Translational evaluation of metabolic risk factors impacting DBS efficacy for PD-related sleep and depressive disorders: preclinical, prospective and cohort studies.Int J Surg. 2025 Jan 1;111(1):543-566. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002081. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39248306 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

