Transcriptomic analysis of the effect of remote ischaemic conditioning in an animal model of necrotising enterocolitis
- PMID: 38734725
- PMCID: PMC11088709
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-61482-9
Transcriptomic analysis of the effect of remote ischaemic conditioning in an animal model of necrotising enterocolitis
Abstract
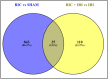
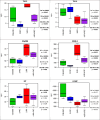
Necrotising enterocolitis (NEC) has a complex pathophysiology but the common end-point is ischaemia reperfusion injury (IRI) and intestinal necrosis. We have previously reported that RIC significantly reduces the intestinal injury in a rat model of NEC. Here we describe the changes in intestinal mRNA occurring in the intestine of animals exposed to IRI, both with and without RIC. Related rat-pups were randomly assigned to four groups: SHAM, IRI only, RIC only and RIC + IRI. IRI animals, underwent 40 min of intestinal ischaemia, and 90 min of reperfusion. Animals that underwent RIC had three cycles of 5 min of alternating ischaemia/reperfusion by means of a ligature applied to the hind limb. Samples from the terminal ileum were immediately stored in RNA-preserving media for later next generation sequencing and transciptome analysis using R v 3.6.1. Differential expression testing showed that 868 genes differentially expressed in animals exposed to RIC alone compared to SHAM and 135 in the IRI and RIC group compared to IRI alone. Comparison between these two sets showed that 25 genes were differentially expressed in both groups. Pro-inflammatory molecules: NF-ĸβ2, Cxcl1, SOD2 and Map3k8 all show reduced expression in response to RIC. Targeted gene analysis revealed increased expression in PI3K which is part of the so-called RISK-pathway which is a key part of the protective mechanisms of RIC in the heart. Overall, this transcriptomic analysis shows that RIC provides a protective effect to the intestine via anti-inflammatory pathways. This could be particularly relevant to treating and preventing NEC.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Remote Ischaemic Pre-Conditioning Reduces Intestinal Ischaemia Reperfusion Injury in a Newborn Rat.J Pediatr Surg. 2023 Jul;58(7):1389-1398. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2022.11.014. Epub 2022 Dec 6. J Pediatr Surg. 2023. PMID: 36621342
-
Remote Ischemic Conditioning (RIC) Decreases the Incidence and Severity of Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) - Validation in a Large Animal Model.J Pediatr Surg. 2025 Jan;60(1):161957. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2024.161957. Epub 2024 Sep 24. J Pediatr Surg. 2025. PMID: 39368858
-
Per- and post-remote ischemic conditioning attenuates ischemic brain injury via inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway in aged rats.Exp Brain Res. 2021 Aug;239(8):2561-2567. doi: 10.1007/s00221-021-06150-4. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Exp Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 34185099
-
Protection of organs other than the heart by remote ischemic conditioning.J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2013 Mar;14(3):193-205. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0b013e328359dd7b. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 2013. PMID: 23079610 Review.
-
Remote ischemic conditioning in necrotizing enterocolitis.Semin Pediatr Surg. 2023 Jun;32(3):151312. doi: 10.1016/j.sempedsurg.2023.151312. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2023. PMID: 37295298 Review.
References
-
- Granger CL, Bowker G, Powls A. G198(P)Express yourself: A quality improvement project aimed at early breast milk expression. Arch. Dis. Childhood. 2018;103(Suppl_1):1–81.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

