Reduction of APOE accounts for neurobehavioral deficits in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders
- PMID: 38734844
- PMCID: PMC11541007
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-024-02586-6
Reduction of APOE accounts for neurobehavioral deficits in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders
Abstract
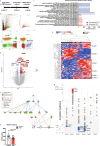
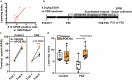
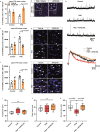
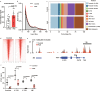
A hallmark of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD) is neurobehavioral deficits that still do not have effective treatment. Here, we present that reduction of Apolipoprotein E (APOE) is critically involved in neurobehavioral deficits in FASD. We show that prenatal alcohol exposure (PAE) changes chromatin accessibility of Apoe locus, and causes reduction of APOE levels in both the brain and peripheral blood in postnatal mice. Of note, postnatal administration of an APOE receptor agonist (APOE-RA) mitigates motor learning deficits and anxiety in those mice. Several molecular and electrophysiological properties essential for learning, which are altered by PAE, are restored by APOE-RA. Our human genome-wide association study further reveals that the interaction of PAE and a single nucleotide polymorphism in the APOE enhancer which chromatin is closed by PAE in mice is associated with lower scores in the delayed matching-to-sample task in children. APOE in the plasma is also reduced in PAE children, and the reduced level is associated with their lower cognitive performance. These findings suggest that controlling the APOE level can serve as an effective treatment for neurobehavioral deficits in FASD.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Popova S, Lange S, Probst C, Gmel G, Rehm J. Estimation of national, regional, and global prevalence of alcohol use during pregnancy and fetal alcohol syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2017;5:e290–e299. - PubMed
-
- Abel EL. An update on incidence of FAS: FAS is not an equal opportunity birth defect. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 1995;17:437–43. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31AA027693/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- U01 AA021886/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA026272/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA014834/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AA014834/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- U24AA030169/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- U01 AA014835/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P50HD105328/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- U01AA014835/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 AA025215/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AA026272/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- U01 AA026103/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AA025215/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- U01AA014809/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- U01AA025103/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- P50 HD105328/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AA030169/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA014809/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AA027693/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

