Somatic mutational profiling and clinical impact of driver genes in Latin-Iberian medulloblastomas: Towards precision medicine
- PMID: 38736183
- PMCID: PMC11788001
- DOI: 10.1111/neup.12979
Somatic mutational profiling and clinical impact of driver genes in Latin-Iberian medulloblastomas: Towards precision medicine
Abstract
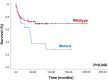
Medulloblastoma (MB) is the most prevalent malignant brain tumor in children, known for its heterogeneity and treatment-associated toxicity, and there is a critical need for new therapeutic targets. We analyzed the somatic mutation profile of 15 driver genes in 69 Latin-Iberian molecularly characterized medulloblastomas using the Illumina TruSight Tumor 15 panel. We classified the variants based on their clinical impact and oncogenicity. Among the patients, 66.7% were MBSHH, 13.0% MBWNT, 7.3% MBGrp3, and 13.0% MBGrp4. Among the 63 variants found, 54% were classified as Tier I/II and 31.7% as oncogenic/likely oncogenic. We observed 33.3% of cases harboring at least one mutation. TP53 (23.2%, 16/69) was the most mutated gene, followed by PIK3CA (5.8%, 4/69), KIT (4.3%, 3/69), PDGFRA (2.9%, 2/69), EGFR (1.4%, 1/69), ERBB2 (1.4%, 1/69), and NRAS (1.4%, 1/69). Approximately 41% of MBSHH tumors exhibited mutations, TP53 (32.6%) being the most frequently mutated gene. Tier I/II and oncogenic/likely oncogenic TP53 variants were associated with relapse, progression, and lower survival rates. Potentially actionable variants in the PIK3CA and KIT genes were identified. Latin-Iberian medulloblastomas, particularly the MBSHH, exhibit higher mutation frequencies than other populations. We corroborate the TP53 mutation status as an important prognostic factor, while PIK3CA and KIT are potential therapeutic targets.
Keywords: medulloblastoma; mutational profile; next‐generation sequencing; precision medicine; somatic variants.
© 2024 The Authors. Neuropathology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Society of Neuropathology.
Figures

References
-
- Global Cancer Observatory: cancer today . Brain, Central Nervous System. Lyon: WHO/IARC, 2020. Available from: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/31-Brain-central-nervo....
-
- Northcott PA, Robinson GW, Kratz CP et al. Medulloblastoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2019; 5: 11. - PubMed
-
- Cotter JA, Hawkins C. Medulloblastoma: WHO 2021 and beyond. Pediatr Dev Pathol 2022; 25: 23–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

