Glutamine promotes human CD8+ T cells and counteracts imiquimod-induced T cell hyporesponsiveness
- PMID: 38736545
- PMCID: PMC11088342
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109767
Glutamine promotes human CD8+ T cells and counteracts imiquimod-induced T cell hyporesponsiveness
Abstract
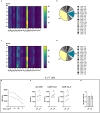
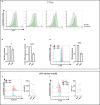
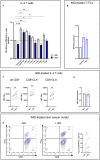
T cells protect tissues from cancer. Although investigations in mice showed that amino acids (AA) critically regulate T cell immunity, this remains poorly understood in humans. Here, we describe the AA composition of interstitial fluids in keratinocyte-derived skin cancers (KDSCs) and study the effect of AA on T cells using models of primary human cells and tissues. Gln contributed to ∼15% of interstitial AAs and promoted interferon gamma (IFN-γ), but not granzyme B (GzB) expression, in CD8+ T cells. Furthermore, the Toll-like receptor 7 agonist imiquimod (IMQ), a common treatment for KDSCs, down-regulated the metabolic gatekeepers c-MYC and mTORC1, as well as the AA transporter ASCT2 and intracellular Gln, Asn, Ala, and Asp in T cells. Reduced proliferation and IFN-γ expression, yet increased GzB, paralleled IMQ effects on AA. Finally, Gln was sufficient to promote IFN-γ-production in IMQ-treated T cells. Our findings indicate that Gln metabolism can be harnessed for treating KDSCs.
Keywords: Dermatology; Immunology.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist related to this study.
Figures



References
-
- Edwards D.N., Ngwa V.M., Raybuck A.L., Wang S., Hwang Y., Kim L.C., Cho S.H., Paik Y., Wang Q., Zhang S., et al. Selective glutamine metabolism inhibition in tumor cells improves antitumor T lymphocyte activity in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Clin. Invest. 2021;131 doi: 10.1172/JCI140100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

