Acute Effects of Loaded and Unloaded Whole-Body Vibration on Vertical Jump Performance in Karate Athletes
- PMID: 38736596
- PMCID: PMC11079925
- DOI: 10.5114/jhk/172637
Acute Effects of Loaded and Unloaded Whole-Body Vibration on Vertical Jump Performance in Karate Athletes
Abstract
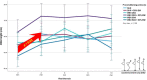
We investigated the acute effects of different whole-body vibration (WBV) interventions on the jump height of highly trained karate practitioners. Fifteen male karate club athletes (age: 20.0 ± 3.8 years; stature: 177.3 ± 4.7 cm; body mass: 76.9 ± 11.2 kg; % body fat: 9.2 ± 4.3) performed six randomized interventions: [a] static half-squat (SHS); [b] SHS with external loads at 30% of the body weight (SHS + 30%BW); [c] WBV at frequency (f) 25 Hz, and 2 mm amplitude (A) (WBV 25/2); [d] WBV 25/2 with external loads of 30% of the body weight (WBV 25/2 + 30% BW); [e] WBV at f = 50 Hz, and A = 4 mm (WBV 50/4), and [f] WBV 50/4 with external loads of 30% of the body weight (WBV 50/4 + 30% BW). Each intervention was performed for 5 sets at 60 s/set, with a rest interval of 30 s between sets. Countermovement jump (CMJ) data were collected at 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 min after each preconditioning intervention. Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA revealed a non-significant main effect of intervention [F(5, 10) = 1.44, η2 = 0.42, p = 0.29)] and a significant main effect of the rest interval [F(4, 11) = 3.51, η2 = 0.56, p = 0.04)] on CMJ height. A rest interval of 4 min resulted in significantly higher CMJ values than a rest interval of 2 min (p = 0.031). In conclusion, utilizing a 4-min rest interval irrespective of the intervention schemes may have potential for enhancing jumping performance among highly trained karate athletes.
Keywords: countermovement jump; explosive power; isometric contraction; martial arts; postactivation potentiation enhancement.
Copyright: © Academy of Physical Education in Katowice.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest were reported by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Whole-Body Vibration on Exercise Performance among Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Hum Kinet. 2024 Dec 19;97:27-50. doi: 10.5114/jhk/193514. eCollection 2025 Apr. J Hum Kinet. 2024. PMID: 40463323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute effects of loaded whole body vibration training on performance.Asian J Sports Med. 2015 Mar;6(1):e24054. doi: 10.5812/asjsm.24054. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Asian J Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 25883774 Free PMC article.
-
The acute effect of different frequencies of whole-body vibration on countermovement jump performance.J Strength Cond Res. 2011 Jun;25(6):1592-7. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181df7fac. J Strength Cond Res. 2011. PMID: 21358422 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of different postactivation potentiation protocols with and without whole body vibration on jumping performance in college athletes.J Strength Cond Res. 2014 Jan;28(1):232-9. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e318295d7fb. J Strength Cond Res. 2014. PMID: 23591951 Clinical Trial.
-
Physical and physiological profile of elite karate athletes.Sports Med. 2012 Oct 1;42(10):829-43. doi: 10.1007/BF03262297. Sports Med. 2012. PMID: 22901041 Review.
Cited by
-
Current trends in physical and physiological profile of elite WKF karate athletes: a systematic review.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025 Jan 10;17(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13102-024-01047-5. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 39794812 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Whole-Body Vibration on Exercise Performance among Athletes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.J Hum Kinet. 2024 Dec 19;97:27-50. doi: 10.5114/jhk/193514. eCollection 2025 Apr. J Hum Kinet. 2024. PMID: 40463323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-activation Performance Enhancement Following Maximal Effort, Multi-Joint Isokinetic Eccentric Muscle Actions.J Hum Kinet. 2025 May 12;97:213-223. doi: 10.5114/jhk/200324. eCollection 2025 Apr. J Hum Kinet. 2025. PMID: 40463309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, J. B., Edwards, D., Serravite, D. H., Bedient, A. M., Huntsman, E., Jacobs, K. A., Del Rossi, G., Roos, B. A., & Signorile, J. F. (2009). Optimal frequency, displacement, duration, and recovery patterns to maximize power output following acute whole-body vibration. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 23(1), 237–245. 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181876830 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Avelar, N. C., Salvado, F. S., Ribeiro, V. G., Vianna, D. M., Costa, S. J., Gripp, F., Coimbra, C. C., & Lacerda, A. C. (2014). Whole body vibration and post-activation potentiation: a study with repeated measures. International Journal of Sports Medicine, 35(8), 651–657. 10.1055/s-0033-1354360 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bedient, A. M., Adams, J. B., Edwards, D., Serviette, D., Huntsman, E., Mow, S. E., Roos, B. A., & Signorile, J. F. (2009). Displacement and frequency for maximizing power output resulting from a bout of whole-body vibration. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 23(6), 1683–1687. 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181b45bdc - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berriel, G. P., Cardoso, A. S., Costa, R. R., Rosa, R. G., Oliveira, H. B., Kruel, L. F. M., & Peyré-Tartaruga, L. A. (2022). Effects of Postactivation Performance Enhancement on The Vertical Jump in High-Level Volleyball Athletes. Journal of Human Kinetics, 82, 145–153. 10.2478/hukin-2022-0041 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
