Manual Therapy in Primary Dysmenorrhea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 38736680
- PMCID: PMC11088071
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S457381
Manual Therapy in Primary Dysmenorrhea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: This research aimed to assess the effectiveness of manual therapy in alleviating pain among women undergoing primary dysmenorrhea (PD).
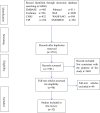
Methods: All randomized controlled trials (RCTs) regarding manual therapy for PD were searched from online databases, spanning from their inception to July 2023. The identified literature underwent a thorough screening process, and the data were meticulously extracted and analyzed using RevMan 5.3. Subsequently, the included studies underwent Cochrane's quality assessment and meta-analysis. The evidence obtained was then assessed using the grading of recommendations, assessment, development, and evaluation (GRADE) approach.
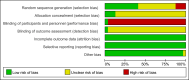
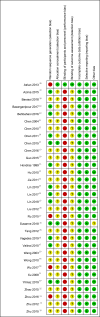
Results: 32 RCTs, involving 2566 women were finally included for analysis. The overall quality of the concluding evidence was generally rated as low or very low. Performance bias and blind bias were found to be the main risk of bias of the included studies. In comparison to no treatment, manual therapy demonstrated a significant increase in pain relief in short-term (n=191, MD=1.30, 95% CI: 0.24~2.37). The differences in the effects of manual therapy and the placebo on pain intensity may not be statistically significant (n=255, MD=0.10, 95% CI: -0.37~0.58). In contrast to NSAIDs, manual therapy exhibited superior pain alleviation (n=507, MD=3.01, 95% CI: 1.08~4.94) and a higher effective rate (n=1029, OR=4.87, 95% CI: 3.29~7.20). Importantly, no severe adverse events were reported across all studies, indicating a relatively safe profile for manual therapy.
Conclusion: Manual therapy presented promise in effectively relieving menstrual pain with minimal adverse events in short term, outperforming both no treatment and NSAIDs. However, this conclusion is tempered by the low quality of the included RCTs, highlighting the necessity for more robust trials to validate it.
Keywords: manual therapy; meta-analysis; primary dysmenorrhea; systematic review.
© 2024 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures




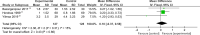




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

