Squaric esters as peptide stapling reagents
- PMID: 38736688
- PMCID: PMC11087058
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2024.155010
Squaric esters as peptide stapling reagents
Abstract
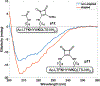
We report that squaric esters can serve as bifunctional reagents for selective peptide stapling reactions. Formation of the squaric amide staple occurs under mild conditions with amine-containing side chains. We show that short resin-bound peptides are readily stapled on solid phase and that stapling can occur at various relative positions along the peptide and with various amine tether lengths (e.g. Lysine, ornithine, etc). The squaric amide staples are stable to strong acid conditions used to cleave the stapled peptide from the resin and the stapled peptides show an increase in helicity as analyzed through circular dichroism.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare that there are no financial conflicts of interest with the present work. Declaration of interests The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: David J Michaelis reports financial support was provided by National Institutes of Health. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Lau JL; Dunn MK Bioorg. Med. Chem. 26 (2018) 2700–2707. - PubMed
-
- Fosgerau K; Hoffmann T 20 (2015) 122–128. - PubMed
-
- Rafferty J; Nagaraj H; McCloskey AP; Huwaitat R; Porter S; Albadr A; Laverty G Curr Med Chem. 23 (2016) 4231–4259. - PubMed
-
- Turecek PL; Bossard MJ; Schoetens F; Ivens IA J. Pharm. Sci. 105 (2016) 460–475. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources