Prognostic and diagnostic effects of high serum midkine levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 38736738
- PMCID: PMC11082639
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2024.14416
Prognostic and diagnostic effects of high serum midkine levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
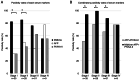
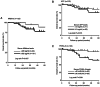
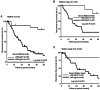
Midkine (MK) is a soluble cytokine, and its serum levels strongly correspond to protein expression levels in tumors. The present study aimed to clarify the clinicopathological and prognostic significance of serum MK (s-MK) in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Serum samples were obtained before surgery from 123 patients with HCC who had undergone surgery between January 2012 and December 2020. The receiver operating characteristic curve revealed that the best cut-off value for s-MK in differentiating HCC from healthy cases was 426 pg/ml. The clinicopathological variables and overall survival of patients were compared between the s-MK-positive group and s-MK-negative group. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of s-MK were 82.1, 97.4 and 88.0%, respectively. An s-MK-positive status was significantly associated with the number of tumors (≥2). The positivity rate of s-MK was significantly higher compared with that of α-fetoprotein and protein-induced by vitamin K absence-II. In total, only 28% of the patients were positive for s-MK. The s-MK-positive group showed significantly worse overall survival compared with the s-MK-negative group. Moreover, multivariate analysis revealed that an s-MK-positive status was independently associated with poor prognosis. s-MK was useful in detecting early HCC. The findings of this study indicated that the s-MK-positive status is associated with the number of tumors and can act as an independent prognostic risk factor.
Keywords: diagnosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; midkine; prognosis; tumor marker.
Copyright © 2024, Spandidos Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Kadomatsu K. Midkine, a heparin-binding growth factor: Its discovery and functions. Seikagaku. 1998;70:1315–1325. (In Japanese) - PubMed
-
- Okada R, Otsuka Y, Wakabayashi T, Shinoda M, Aoki T, Murakami M, Arizumi S, Yamamoto M, Aramaki O, Takayama T, et al. Six autoantibodies as potential serum biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective multicenter study. Int J Cancer. 2020;147:2578–2586. doi: 10.1002/ijc.33165. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
