Effect of iron saturation of bovine lactoferrin on the inhibition of hepatitis B virus in vitro
- PMID: 38737747
- PMCID: PMC11086297
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.17302
Effect of iron saturation of bovine lactoferrin on the inhibition of hepatitis B virus in vitro
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection poses a major public health problem worldwide. Bovine lactoferrin (bLf) is a natural product that can inhibit HBV, but the effect of iron saturation on its resistance to HBV is unknown.
Aims: The purpose of this study is to investigate the impact of iron saturation of bLf against HBV.
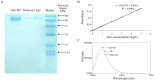
Methods: HepG2 cells were cultured in DMEM high glucose containing 10% inactivated fetal calf serum, at 37 °C, in 5% CO2. MTT method was used to detect the cytotoxicity of bLf to HepG2 cells. Apo-bLf and holo-bLf were prepared from bLf. Iron saturation of these proteins was determined by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Non-cytotoxic concentrations of candidate proteins were used in anti-HBV tests. Fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to detect HBV-DNA.
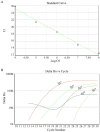
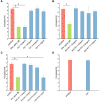
Results: The TC50 and TC0of bLf were 54.570 mg/ml and 1.997 mg/ml, respectively. The iron saturation of bLf, apo-bLf and holo-bLf were 10.29%, 8.42% and 85.32%, respectively. In this study, four non-cytotoxic concentrations of candidate proteins (1.5, 1.0, 0.5, and 0.1 mg/ml, respectively) were used to inhibit HBV in HepG2 cells. The results showed that 1.5 mg/ml bLf and 0.1 mg/ml holo-bLf effectively impaired the HBV-DNA amplification in HBV-infected HepG2 cells (P < 0.05). However, apo-bLf, and Fe3+ did not show the anti-HBV effects.
Conclusion: A total of 1.5 mg/ml bLf and 0.1 mg/ml holo-bLf could inhibit HBV-DNA in HepG2 cells. Complete bLf structure, appropriate concentration and iron saturation of bLf are necessary conditions for anti-HBV effects.
Keywords: Bovine lactoferrin; HepG2 cell; Hepatitis B virus; Iron saturation; Polymerase chain reaction.
©2024 Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Yiwei Zhu is an employee of Chongqing Food Industry Research Institute Co., Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Study of inhibition effect of zinc-, iron- and manganese-saturated bovine lactoferrin on hepatitis B virus DNA in vitro].Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2008 Sep;37(5):586-9. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2008. PMID: 19069661 Chinese.
-
Inhibition of HBV infection by bovine lactoferrin and iron-, zinc-saturated lactoferrin.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2009 Feb;198(1):19-25. doi: 10.1007/s00430-008-0100-7. Epub 2008 Sep 23. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 18810491
-
[Study of inhibition effect of bovine lactoferrin in vitro on hepatitis B surface antigen].Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2008 Mar;37(2):196-8. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2008. PMID: 18589607 Chinese.
-
The Multifaceted Roles of Bovine Lactoferrin: Molecular Structure, Isolation Methods, Analytical Characteristics, and Biological Properties.J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Dec 27;71(51):20500-20531. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c06887. Epub 2023 Dec 13. J Agric Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 38091520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactoferrin: A Natural Glycoprotein Involved in Iron and Inflammatory Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 15;18(9):1985. doi: 10.3390/ijms18091985. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28914813 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lactoferrin: A Promising Therapeutic Molecule against Human Papillomavirus.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 12;16(18):3073. doi: 10.3390/nu16183073. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of lactoferrin as antiviral and immune-modulating agent in viral infectious diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 15;15:1402135. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1402135. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39620218 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ascione A, Ascione T, Lanza AG, Utech W, Di Costanzo GG, Macri M. Factors influencing outcome of lamivudine in anti-HBe-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatogastroenterology. 2006;53(72):919–923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

