Accurate etiological diagnosis of Mycoplasma hominis mediastinitis in immunocompetent patients using metagenomic next-generation sequencing: a case series and literature review
- PMID: 38738251
- PMCID: PMC11087618
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd-24-286
Accurate etiological diagnosis of Mycoplasma hominis mediastinitis in immunocompetent patients using metagenomic next-generation sequencing: a case series and literature review
Abstract
Background: As a culture-independent method, metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) is widely used in microbiological diagnosis with advantages in identifying potential pathogens, guiding antibiotic therapy, and improving clinical prognosis, especially in culture-negative cases. Mycoplasma hominis (M. hominis) mediastinitis is a rare and severe disease for which etiological diagnosis is important but challenging. The application of mNGS in the etiological diagnosis of mediastinitis has seldom been studied.
Methods: By searching the electronic medical history retrieval system with "Mycoplasma hominis" and "mediastinitis", seven patients diagnosed with M. hominis mediastinitis were reviewed in Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai from 9 December 2020 to 14 February 2023. Microbiological cultures and mNGS were conducted for blood, abscess, and/or mediastinal fluid. Adjustment of the antibiotic therapy due to mNGS was assessed. A literature review was conducted in the PubMed database beginning in 1970 for M. hominis infection and mediastinitis.
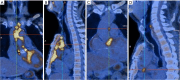
Results: For the seven patients, cultures of blood, abscess, and mediastinal fluid were negative whereas mNGS identified M. hominis in serum, abscess, and/or mediastinal fluid and was used to guide specific antibiotic therapy. The stringent mapped reads number of genera (SMRNG), stringent mapped reads number of species (SMRN), and coverage rate of M. hominis detection by mNGS were significantly higher in body fluid (abscess or mediastinal fluid) than in serum. All seven patients had underlying heart diseases and underwent previous cardiac surgery. The most common symptoms were fever and sternal pain. After detection of M. hominis, antibiotics were adjusted to quinolones or doxycycline except for one patient, whose diagnosis was clarified after death. Two patients died. Literature review since 1970 identified 30 cases of extra-genital infection caused by M. hominis. Including our seven new cases, 2 (5.4%) were neonates and 35 (94.6%) were adults. Thirty (81.1%) cases were postoperative infection and 15 (40.5%) had implanted devices. Five patients (13.5%) died.
Conclusions: mNGS might be a promising technology in the detection of fastidious pathogens such as M. hominis. Accurate etiological diagnosis by mNGS could guide antibiotic therapy and facilitate clinical management.
Keywords: Metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS); Mycoplasma hominis (M. hominis); case series; diagnosis; mediastinitis.
2024 Journal of Thoracic Disease. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jtd.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jtd-24-286/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intracranial infection in an adult caused by Mycoplasma hominis, diagnosed using mNGS technology: a case report.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 4;12:1560635. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1560635. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40103786 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical value of valve metagenomic next-generation sequencing when applied to the etiological diagnosis of infective endocarditis.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Oct;9(19):1490. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-2488. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34805352 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of Mycoplasma hominis Meningitis with Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing: A Case Report.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Aug 12;15:4479-4486. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S371771. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 35983300 Free PMC article.
-
Mycoplasma hominis Meningitis Diagnosed by Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing in a Preterm Newborn: a Case Report and Literature Review.Lab Med. 2023 Jan 5;54(1):e24-e28. doi: 10.1093/labmed/lmac078. Lab Med. 2023. PMID: 35801947 Review.
-
Mycoplasma hominis infections occurring in cardiovascular surgical patients.Ann Thorac Surg. 1996 Jan;61(1):99-103. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(95)00826-8. Ann Thorac Surg. 1996. PMID: 8561647 Review.
Cited by
-
Intracranial infection in an adult caused by Mycoplasma hominis, diagnosed using mNGS technology: a case report.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 4;12:1560635. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1560635. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40103786 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
