A comparison of the activity, lysosomal stability, and efficacy of legumain-cleavable and cathepsin-cleavable ADC linkers
- PMID: 38738708
- PMCID: PMC11436314
- DOI: 10.1080/00498254.2024.2352051
A comparison of the activity, lysosomal stability, and efficacy of legumain-cleavable and cathepsin-cleavable ADC linkers
Abstract
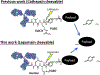
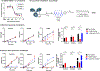
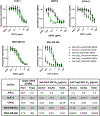
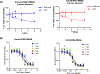
Over the past two decades, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) have emerged as a highly effective drug delivery technology. ADCs utilise a monoclonal antibody, a chemical linker, and a therapeutic payload to selectively deliver highly potent pharmaceutical agents to specific cell types.Challenges such as premature linker cleavage and clearance due to linker hydrophobicity have adversely impacted the stability and safety of ADCs. While there are various solutions to these challenges, our team has focused on replacement of hydrophobic ValCit linkers (cleaved by CatB) with Asn-containing linkers that are cleaved by lysosomal legumain.Legumain is abundantly present in lysosomes and is known to play a role in tumour microenvironment dynamics. Herein, we directly compare the lysosomal cleavage, cytotoxicity, plasma stability, and efficacy of a traditional cathepsin-cleavable ADC to a matched Asn-containing legumain-cleavable ADC.We demonstrate that Asn-containing linker sequences are specifically cleaved by lysosomal legumain and that Asn-linked MMAE ADCs are broadly active against a variety of tumours, even those with low legumain expression. Finally, we show that AsnAsn-linked ADCs exhibit comparable or improved efficacy to traditional ValCit-linked ADCs. Our study paves the way for replacement of the traditional ValCit linker technology with more hydrophilic Asn-containing peptide linker sequences.
Keywords: ADC; Antibody–drug conjugate; MMAE; cancer; cathepsin B; legumain; linker.
Figures
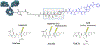
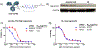

References
-
- AbbVie Takes $4B Hit on Rova-T Failures | FierceBiotech. 2019. Accessed February 18. https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/abbvie-takes-4b-hit-rova-t-failures.
-
- Alvarez-Fernandez Marcia, Barrett Alan J., Gerhartz Bernd, Dando Pam M., Ni Jian, and Abrahamson Magnus. 1999. Inhibition of Mammalian Legumain by Some Cystatins Is Due to a Novel Second Reactive Site. Journal of Biological Chemistry 274 (27). Elsevier:19195–19203. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.27.19195. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anami Yasuaki, Yamazaki Chisato M., Xiong Wei, Gui Xun, Zhang Ningyan, An Zhiqiang, and Tsuchikama Kyoji. 2018. Glutamic Acid-Valine-Citrulline Linkers Ensure Stability and Efficacy of Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Mice. Nature Communications 9 (1):2512. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04982-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamin SR. Samantha R, Jackson Courtney P C.P., Fang Siteng, Carlson Dane P D.P., Guo Zhongyuan, and Nathan Tumey LN. 2019. Thiolation of Q295: Site-Specific Conjugation of Hydrophobic Payloads without the Need for Genetic Engineering. Molecular Pharmaceutics 16 (6). American Chemical Society:2795–2807. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00323. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
