Discordant results between Xpert MTB/RIF assay and Bactec MGIT 960 culture system regarding the detection of rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates in Wenzhou, China
- PMID: 38738892
- PMCID: PMC11237732
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.03859-23
Discordant results between Xpert MTB/RIF assay and Bactec MGIT 960 culture system regarding the detection of rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates in Wenzhou, China
Abstract
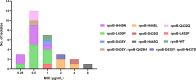
This study aimed to assess the possible causes of discordant results between Xpert MTB/RIF (Xpert) and Bactec MGIT 960 Culture System (MGIT960) regarding rifampicin (RIF) susceptibility in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Patients with previous RIF-resistant tuberculosis who were admitted to Wenzhou Central Hospital from January 2020 to December 2022 were enrolled. The isolates obtained from these patients were subjected to RIF susceptibility tests using Xpert and MGIT960, and the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of RIF was determined by the MYCOTB MIC plate test. Additionally, molecular docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed to evaluate the binding efficacy of rpoB and RIF based on rpoB mutations detected in the isolates with discordant RIF susceptibility results. A total of 28 isolates with discordant RIF susceptibility test results were detected, 15 of them were RIF susceptible with MICs ≤ 0.5 µg/mL. Twelve out of 15 isolates contained borderline RIF resistance-associated mutations [L430P (n = 6), H445N (n = 6)], 1 isolate had D435Y and Q429H double mutation, and the remaining 2 isolates had a silent (Q432Q) mutation. Compared with the affinity of RIF toward the wild type (WT) (-45.83 kcal/mol) by MD, its affinity toward L452P (-55.52 kcal/mol), D435Y (-47.39 kcal/mol), L430P (approximately -69.72 kcal/mol), H445N (-49.53 kcal/mol), and Q429H (-55.67 kcal/mol) increased. Borderline RIF resistance-associated mutations were the main cause for the discordant RIF susceptibility results between Xpert and MGIT960, and the mechanisms of the resistance need further investigated.IMPORTANCEThis study is aimed at assessing discordant results between Xpert MTB/RIF (Xpert) assay and Bactec MGIT 960 Culture System (MGIT960) regarding the detection of rifampicin (RIF)-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates in Wenzhou, China. The discordant results of RIF between these two assays were mainly caused by borderline RIF resistance-associated mutations, subsequently by silent mutations of rpoB. Borderline RIF resistance- associated mutations detected in our study were demonstrated to not be affected by the affinity of rpoB and RIF by molecular dynamics, and the mechanism of resistance was needed to be clarified. For the discordant results of RIF by Xpert and MGIT960 that occurred, rpoB DNA sequencing was recommended to investigate its association with resistance to RIF.
Keywords: Xpert MTB/RIF assay, Bactec MGIT 960; borderline RIF resistance; drug-resistant tuberculosis; rpoB mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . 2023. Global tuberculosis report 2023. https://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/.
-
- Ahmad N, Ahuja SD, Akkerman OW, Alffenaar J-WC, Anderson LF, Baghaei P, Bang D, Barry PM, Bastos ML, Behera D, et al. 2018. Treatment correlates of successful outcomes in pulmonary multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Lancet 392:821–834. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31644-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mokaddas E, Ahmad S, Eldeen HS, Al-Mutairi N. 2015. Discordance between Xpert MTB/RIF assay and bactec MGIT 960 culture system for detection of rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates in a country with a low tuberculosis (TB) incidence. J Clin Microbiol 53:1351–1354. doi: 10.1128/JCM.03412-14 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

