Enthesitis and Dactylitis Resolution with Risankizumab for Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Integrated Analysis of the Randomized KEEPsAKE 1 and 2 Trials
- PMID: 38739215
- PMCID: PMC11169338
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-024-01174-4
Enthesitis and Dactylitis Resolution with Risankizumab for Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Integrated Analysis of the Randomized KEEPsAKE 1 and 2 Trials
Abstract
Introduction: The presence (vs absence) of enthesitis/dactylitis is associated with greater psoriatic arthritis (PsA) activity and reduced health-related quality of life. Risankizumab, an interleukin 23 antagonist, demonstrated superior treatment efficacy over placebo in patients with PsA, including enthesitis/dactylitis. Herein, we report the efficacy of risankizumab on complete resolution of enthesitis and/or dactylitis and improvements in patient-reported outcomes in patients with PsA.
Methods: This integrated post hoc analysis of data from KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2 included patients with baseline enthesitis (Leeds Enthesitis Index > 0) and/or dactylitis (Leeds Dactylitis Index > 0). Efficacy outcomes at weeks 24 and 52 included proportion of patients achieving enthesitis and/or dactylitis resolution and minimal clinically important differences (MCID) in pain, Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index, and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue.
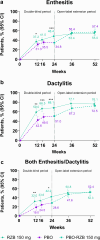
Results: Of 1407 patients, approximately 63%, 28%, and 20% had baseline enthesitis, dactylitis, and both enthesitis/dactylitis, respectively. At week 24, higher response rates were observed for risankizumab vs placebo for resolution of enthesitis, dactylitis, and both enthesitis/dactylitis (differences of 13.9%, 16.9%, and 13.3%, respectively; p < 0.05). By week 52, risankizumab treatment resulted in complete resolution of enthesitis, dactylitis, and both enthesitis and dactylitis in 55.0%, 76.1%, and 52.3% of patients; similar resolution rates occurred among patients who switched from placebo to risankizumab. Among risankizumab-treated patients who achieved resolution of enthesitis and/or dactylitis, MCIDs were also attained in patient-reported pain, disability, and fatigue at week 24 (all p < 0.05; except fatigue in patients with resolution of both enthesitis/dactylitis); responses were sustained through week 52.
Conclusions: Higher proportions of risankizumab-treated (vs placebo-treated) patients achieved enthesitis and/or dactylitis resolution and meaningful improvements in patient-reported outcomes at week 24 and generally sustained responses at week 52. Thus, risankizumab may result in sustained alleviation of PsA-related pathognomonic musculoskeletal lesions of enthesitis/dactylitis.
Gov identifiers: NCT03675308, and NCT03671148.
Keywords: Biologic; Dactylitis; Enthesitis; Interleukin 23; Psoriasis; Psoriatic arthritis; Risankizumab.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Shawn G. Kwatra is an advisory board member/consultant and/or investigator for AbbVie, Arcutis, ASLAN, Celldex, Galderma, Genzada, Incyte, J&J, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi. Saakshi Khattri is a speaker, serves as an advisory board member for, and/or has received research grants from AbbVie, BMS, Janssen, LEO, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB. Ahmad Z. Amin has received speaker or consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Dermavant, Incyte, Janssen, LEO, Lilly, Regeneron, Sanofi-Genzyme, Pfizer, and UCB. Roberto Ranza is a consultant for AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, and Pfizer, and is a member of speaker bureaus for AbbVie, Janssen, Novartis, and Pfizer. Blair Kaplan, Linyu Shi, Byron Padilla, and Ahmed M. Soliman are employees of AbbVie, and may hold AbbVie stock, stock options, and/or patents. Dennis McGonagle has received research grants from and/or is a member of speaker bureaus for AbbVie, BMS, Celgene, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
Figures

References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

