Treatment approach and outcomes of patients with accelerated/blast-phase myeloproliferative neoplasms in the current era
- PMID: 38739724
- PMCID: PMC11260843
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024012880
Treatment approach and outcomes of patients with accelerated/blast-phase myeloproliferative neoplasms in the current era
Abstract
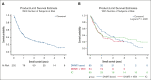
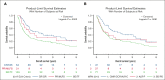
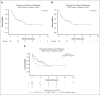
Progression of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) to accelerated or blast phase is associated with poor survival outcomes. Since 2017 there have been several therapies approved for use in acute myeloid leukemia (AML); these therapies have been incorporated into the management of accelerated/blast-phase MPNs (MPN-AP/BP). We performed a multicenter analysis to investigate outcomes of patients diagnosed with MPN-AP/BP in 2017 or later. In total, 202 patients were identified; median overall survival (OS) was 0.86 years. We also analyzed patients based on first-line treatment; the 3 most common approaches were intensive chemotherapy (n = 65), DNA methyltransferase inhibitor (DNMTi)-based regimens (n = 65), and DNMTi + venetoclax-based regimens (n = 54). Median OS was not significantly different by treatment type. In addition, we evaluated response by 2017 European LeukemiaNet AML criteria and 2012 MPN-BP criteria in an effort to understand the association of response with survival outcomes. We also analyzed outcomes in 65 patients that received allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (allo-HSCT); median OS was 2.30 years from time of allo-HSCT. Our study demonstrates that survival among patients with MPN-AP/BP is limited in the absence of allo-HSCT even in the current era of therapeutics and underscores the urgent need for new agents and approaches.
© 2024 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A.A.P. received honoraria from AbbVie and Bristol Myers Squibb, and research funding (institutional) from Pfizer and Kronos Bio. R.M.S. received honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Kura Oncology, Gilead Sciences, Rigel, and Servier. E.C.C. received consulting fees from AbbVie and Rigel. S.G.I. received honoraria from Medical Logix (medical education) and reports an advisory board role with MorphoSys. R.K.R. received research funding from Incyte, Constellation, Zentalis, Stemline, and Ryyu, and received consulting fees from Celgene-Bristol Myers Squibb, Kartos, Zentalis, Karyopharm, Dainippon, GlaxoSmithKline-Sierra, Galecto, Pharmessentia, Incyte, CTI Biopharma, Servier, MorphoSys/Constellation, and Sumitumo. T.B. reports membership on advisory committee for Novartis, Geron Corporation, and Gilead, and speakers bureau for Novartis. Y.A. received research funding from Biomea, Curis, Biosight, and ALX Oncology Novartis, and honoraria from Servier, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Kite, Astellas, and Rigel. J.S.G. received research funding from AbbVie, Genentech, New Wave, Pfizer, and Prelude, and served on steering committee/scientific advisory board for AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech, and Servier. V.G. received research funding from AbbVie and Novartis; reports consulting fees from Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Keros, AbbVie, Constellation Biopharma, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, and CTI Biopharma; reports honoraria from Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, and AbbVie; and serves on the data safety monitoring or advisory board for Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Roche, AbbVie, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, and CTI Biopharma. K.M.P. reports consulting fees from Protagonist Therapeutics and AbbVie; received research funding from Protagonist Therapeutics, Merck, and AbbVie; and reports speakers bureau membership with Merck. O.O. reports consulting fees from AbbVie, Blueprint Medicines, Bristol Myers Squibb, CTI, Impact Biomedicines, Kymera, Novartis, SERVIER, Taiho Pharmaceutical, and Threadwell Therapeutics; and received research funding (to institution) from AbbVie, Agios, Aprea AB, Astex Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, CTI BioPharma Corp, Daiichi Sankyo, Incyte, Janssen Oncology, Kartos Therapeutics, Loxo, Novartis, NS Pharma, and OncoTherapy Science. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Patel AA, Odenike O. SOHO state of the art updates and next questions | accelerated phase of MPN: what it is and what to do about it. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2023;23(5):303–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

