Plasmid targeting and destruction by the DdmDE bacterial defence system
- PMID: 38740055
- PMCID: PMC11649018
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07515-9
Plasmid targeting and destruction by the DdmDE bacterial defence system
Abstract
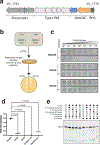
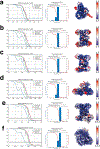
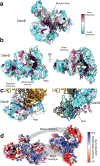
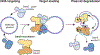
Although eukaryotic Argonautes have a pivotal role in post-transcriptional gene regulation through nucleic acid cleavage, some short prokaryotic Argonaute variants (pAgos) rely on auxiliary nuclease factors for efficient foreign DNA degradation1. Here we reveal the activation pathway of the DNA defence module DdmDE system, which rapidly eliminates small, multicopy plasmids from the Vibrio cholerae seventh pandemic strain (7PET)2. Through a combination of cryo-electron microscopy, biochemistry and in vivo plasmid clearance assays, we demonstrate that DdmE is a catalytically inactive, DNA-guided, DNA-targeting pAgo with a distinctive insertion domain. We observe that the helicase-nuclease DdmD transitions from an autoinhibited, dimeric complex to a monomeric state upon loading of single-stranded DNA targets. Furthermore, the complete structure of the DdmDE-guide-target handover complex provides a comprehensive view into how DNA recognition triggers processive plasmid destruction. Our work establishes a mechanistic foundation for how pAgos utilize ancillary factors to achieve plasmid clearance, and provides insights into anti-plasmid immunity in bacteria.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




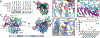

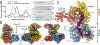

References
Main Text References
Methods references
-
- Mastronarde DN (2005) Automated electron microscope tomography using robust prediction of specimen movements. J Struct Biol, 152, 36–51. - PubMed
-
- Punjani A (2021) Real-time cryo-EM structure determination. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 27, 1156–1157.
-
- Punjani A, Rubinstein JL, Fleet DJ and Brubaker MA (2017) CryoSPARC: Algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination. Nat Methods, 14, 290–296. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

