The role of microRNA-142a in Toxoplasma gondii infection-induced downregulation of Foxp3: implications for adverse pregnancy outcomes
- PMID: 38741041
- PMCID: PMC11089769
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-024-09375-0
The role of microRNA-142a in Toxoplasma gondii infection-induced downregulation of Foxp3: implications for adverse pregnancy outcomes
Abstract
Background: Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) is capable of infecting nearly all warm-blooded animals and approximately 30% of the global population. Though most infections are subclinical in immunocompetent individuals, congenital contraction can lead to severe consequences such as spontaneous abortion, stillbirth, and a range of cranio-cerebral and/or ocular abnormalities. Previous studies reported that T. gondii-infected pregnancy mice unveiled a deficit in both the amount and suppressive functions of regulatory T (Treg) cells, accompanied with reduced levels of forkhead box p3 (Foxp3). Recently, accumulative studies have demonstrated that microRNAs (miRNAs) are, to some extent, relevant to T. gondii infection. However, the link between alterations in miRNAs and downregulation of Foxp3 triggered by T. gondii has been only sporadically studied.
Methods: Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), protein blotting and immunofluorescence were employed to evaluate the impact of T. gondii infection and antigens on miRNA transcription and Foxp3 expression. Dual-luciferase reporter gene assays were performed to examine the fluorescence activity in EL4 cells, which were transfected with recombinant plasmids containing full-length/truncated/mutant microRNA-142a-3p (miR-142a) promoter sequence or wild type/mutant of Foxp3 3' untranslated region (3' UTR).
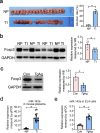
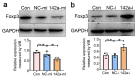
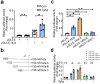
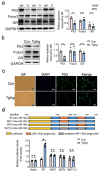
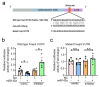
Results: We found a pronounced increase in miR-142a transcription, concurrent with a decrease in Foxp3 expression in T. gondii-infected mouse placental tissue. Similarly, comparable findings have been experimentally confirmed through the treatment of EL4 cells with T. gondii antigens (TgAg) in vitro. Simultaneously, miR-142a mimics attenuated Foxp3 expression, whereas its inhibitors markedly augmented Foxp3 expression. miR-142a promoter activity was elevated upon the stimulation of T. gondii antigens, which mitigated co-transfection of mutant miR-142a promoter lacking P53 target sites. miR-142a mimics deceased the fluorescence activity of Foxp3 3' untranslated region (3' UTR), but it did not affect the fluorescence activity upon the co-transfection of mutant Foxp3 3' UTR lacking miR-142a target site.
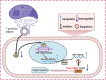
Conclusion: In both in vivo and in vitro studies, a negative correlation was discovered between Foxp3 expression and miR-142a transcription. TgAg enhanced miR-142a promoter activity to facilitate miR-142a transcription through a P53-dependent mechanism. Furthermore, miR-142a directly targeted Foxp3 3' UTR, resulting in the downregulation of Foxp3 expression. Therefore, harnessing miR-142a may be a possible therapeutic approach for adverse pregnancy caused by immune imbalances, particularly those induced by T. gondii infection.
Keywords: Toxoplasma Gondii; Forkhead box P3; P53; microRNA-142a-3p.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Aline Cristina Abreu M-S, Thuany Prado R, Sthefani Rodrigues Batista da S, Vanessa Ribeiro F, Luiz Eduardo Baggio S, Felipe S, Christina Maeda T, Angela TSW, Rossiane Claudia V, Robson C-S. Disruption of Purinergic Receptor P2X7 Signaling Increases Susceptibility to Cerebral Toxoplasmosis. Am J Pathol. 2019; 189(4):730–738. - PubMed
-
- Jingfan Q, Yanci X, Chenlu S, Tianye S, Min Q, Rong Z, Xinjian L, Zhipeng X, Yong W. Toxoplasma Gondii microneme protein MIC3 induces macrophage TNF-α production and Ly6C expression via TLR11/MyD88 pathway. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023;17(2):e0011105. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

