Subcallosal area 25: Its responsivity to the stress hormone cortisol and its opposing effects on appetitive motivation in marmosets
- PMID: 38741617
- PMCID: PMC11089406
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2024.100637
Subcallosal area 25: Its responsivity to the stress hormone cortisol and its opposing effects on appetitive motivation in marmosets
Abstract
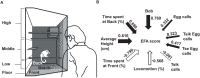
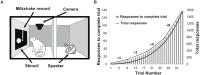
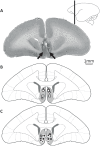
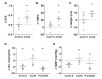
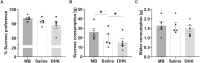
Aberrant activity in caudal subcallosal anterior cingulate cortex (scACC) is implicated in depression and anxiety symptomatology, with its normalisation a putative biomarker of successful treatment response. The function of scACC in emotion processing and mental health is not fully understood despite its known influence on stress-mediated processes through its rich expression of mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors. Here we examine the causal interaction between area 25 within scACC (scACC-25) and the stress hormone, cortisol, in the context of anhedonia and anxiety-like behaviour. In addition, the overall role of scACC-25 in hedonic capacity and motivation is investigated under transient pharmacological inactivation and overactivation. The results suggest that a local increase of cortisol in scACC-25 shows a rapid induction of anticipatory anhedonia and increased responsiveness to uncertain threat. Separate inactivation and overactivation of scACC-25 increased and decreased motivation and hedonic capacity, respectively, likely through different underlying mechanisms. Together, these data show that area scACC-25 has a causal role in consummatory and motivational behaviour and produces rapid responses to the stress hormone cortisol, that mediates anhedonia and anxiety-like behaviour.
Keywords: Anhedonia; Anxiety; Area 25; Depression; Stress; Subcallosal anterior cingulate cortex.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
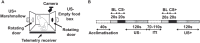


Similar articles
-
Chemogenetics identifies separate area 25 brain circuits involved in anhedonia and anxiety in marmosets.Sci Transl Med. 2023 Apr 5;15(690):eade1779. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.ade1779. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Sci Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37018416 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the presence or absence of atrophy of the subgenual and subcallosal cingulate cortices using voxel-based morphometry on MRI is useful to select prescriptions for patients with depressive symptoms.Int J Gen Med. 2014 Dec 3;7:513-24. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S72736. eCollection 2014. Int J Gen Med. 2014. PMID: 25506239 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal and left subcallosal anterior cingulate atrophy in psychotic depression.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 22;9(10):e110770. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110770. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25338068 Free PMC article.
-
The ventromedial prefrontal cortex and emotion regulation: lost in translation?J Physiol. 2023 Jan;601(1):37-50. doi: 10.1113/JP282627. Epub 2022 Jun 11. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 35635793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Focus on the Functions of Area 25.Brain Sci. 2019 Jun 3;9(6):129. doi: 10.3390/brainsci9060129. Brain Sci. 2019. PMID: 31163643 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexander L., Gaskin P.L.R., Sawiak S.J., Fryer T.D., Hong Y.T., Cockcroft G.J., Clarke H.F., Roberts A.C. Fractionating blunted reward processing characteristic of anhedonia by over-activating primate subgenual anterior cingulate cortex. Neuron. 2018;101:307–320.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.11.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alexander L., Wood C.M., Gaskin P.L.R., Sawiak S.J., Fryer T.D., Hong Y.T., McIver L., Clarke H.F., Roberts A.C. Over-activation of primate subgenual cingulate cortex enhances the cardiovascular, behavioral and neural responses to threat. Nat. Commun. 2020;11 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19167-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

