Local Flaps in Breast-Conserving Surgery in Early Breast Cancer Patients: Armamentarium for Breast Surgeon
- PMID: 38741625
- PMCID: PMC11088574
- DOI: 10.1007/s13193-024-01880-7
Local Flaps in Breast-Conserving Surgery in Early Breast Cancer Patients: Armamentarium for Breast Surgeon
Abstract
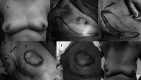
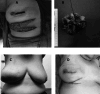
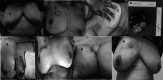
To describe the technique and outcome of local perforator arteries advancement flap in breast-conserving surgeries (BCS) in patient of early breast cancer as our initial experience and review of literature on it. Patients who underwent (BCS) with local perforator artery flap reconstruction were reviewed in terms of their clinical, surgical, and post-operative follow-up details after taking written and informed consent. We have described 4 patients of early breast cancer out of which one patient was post-NACT while 3 were for upfront BCS. We have performed LICAP in 2 patients, AICAP in 1 patient, and IMAP in one patient, depending on the location of primary tumors. None of the patients had any major or minor surgical complications in the post-operative period and drains were removed on post-operative day 2. All patients received post-operative radiotherapy and tolerated well without any loco-regional complications. Patients are in routine follow-up with cosmetic satisfaction without any local recurrence over 1 year. The main advantages of pedicled perforator flaps are well-vascularized tissue, spares underlying muscle leading to lesser donor site morbidity like muscle function and seroma formation, easily reach the breast area with good match in terms of skin and subcutaneous tissue, faster recovery, and shorter learning curve in comparison to free flaps. Knowledge and skill about these flaps will help surgeon to give better surgical outcomes and satisfaction to patients.
Keywords: Armamentarium; Breast surgeon; Breast-conserving surgery.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Indian Association of Surgical Oncology 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
