ALK inhibitors suppress HCC and synergize with anti-PD-1 therapy and ABT-263 in preclinical models
- PMID: 38741708
- PMCID: PMC11089374
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109800
ALK inhibitors suppress HCC and synergize with anti-PD-1 therapy and ABT-263 in preclinical models
Abstract
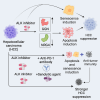
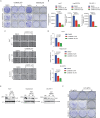
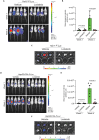
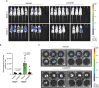
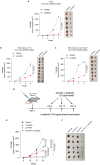
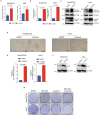
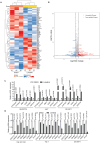
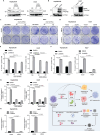
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) currently lacks effective therapies, leaving a critical need for new treatment options. A previous study identified the anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) amplification in HCC patients, raising the question of whether ALK inhibitors could be a viable treatment. Here, we showed that both ALK inhibitors and ALK knockout effectively halted HCC growth in cell cultures. Lorlatinib, a potent ALK inhibitor, suppressed HCC tumor growth and metastasis across various mouse models. Additionally, in an advanced immunocompetent humanized mouse model, when combined with an anti-PD-1 antibody, lorlatinib more potently suppressed HCC tumor growth, surpassing individual drug efficacy. Lorlatinib induced apoptosis and senescence in HCC cells, and the senolytic agent ABT-263 enhanced the efficacy of lorlatinib. Additional studies identified that the apoptosis-inducing effect of lorlatinib was mediated via GGN and NRG4. These findings establish ALK inhibitors as promising HCC treatments, either alone or in combination with immunotherapies or senolytic agents.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Cancer; Cancer systems biology; Natural sciences; Pharmacology; Systems biology.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: results from a global phase 2 study.Lancet Oncol. 2018 Dec;19(12):1654-1667. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30649-1. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Lancet Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30413378 Clinical Trial.
-
Adaptive resistance to lorlatinib via EGFR signaling in ALK-rearranged lung cancer.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2023 Jan 26;7(1):12. doi: 10.1038/s41698-023-00350-7. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36702855 Free PMC article.
-
Combination Therapies Targeting ALK-aberrant Neuroblastoma in Preclinical Models.Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Apr 3;29(7):1317-1331. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2274. Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36602782 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological and clinical properties of lorlatinib in the treatment of ALK-rearranged advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Sep;21(13):1547-1554. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1774552. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32511029 Review.
-
Update on Lorlatinib: Role in Reducing the Risk of Disease Progression in ALK-Positive NSCLC.Cancer Manag Res. 2022 Feb 26;14:843-850. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S283199. eCollection 2022. Cancer Manag Res. 2022. PMID: 35250311 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

