Genome-based surveillance reveals cross-transmission of MRSA ST59 between humans and retail livestock products in Hanzhong, China
- PMID: 38741738
- PMCID: PMC11089119
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1392134
Genome-based surveillance reveals cross-transmission of MRSA ST59 between humans and retail livestock products in Hanzhong, China
Abstract
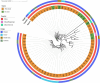
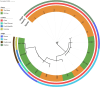
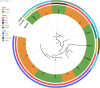
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has been recognized in hospitals, community and livestock animals and the epidemiology of MRSA is undergoing a major evolution among humans and animals in the last decade. This study investigated the prevalence of MRSA isolates from ground pork, retail whole chicken, and patient samples in Hanzhong, China. The further characterization was performed by antimicrobial susceptibility testing and in-depth genome-based analysis to identify the resistant determinants and their phylogenetic relationship. A total of 93 MRSA isolates were recovered from patients (n = 67) and retail livestock products (n = 26) in Hanzhong, China. 83.9% (78/93) MRSA isolates showed multiple drug resistant phenotype. Three dominant livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (LA-MRSA) sequence types were identified: ST59-t437 (n = 47), ST9-t899 (n = 10) and ST398 (n = 7). There was a wide variation among sequence types in the distribution of tetracycline-resistance, scn-negative livestock markers and virulence genes. A previous major human MRSA ST59 became the predominant interspecies MRSA sequence type among humans and retail livestock products. A few LA-MRSA isolates from patients and livestock products showed close genetic similarity. The spreading of MRSA ST59 among livestock products deserving special attention and active surveillance should be enacted for the further epidemic spread of MRSA ST59 in China. Data generated from this study will contribute to formulation of new strategies for combating spread of MRSA.
Keywords: ST398; ST59; ST9; interspecies transmission; livestock-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Wang, Zhao, Gu, Chen, Liu, An, Bai, Chen and Cui.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genomic epidemiology and characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from raw milk in Jiangsu, China: emerging broader host tropism strain clones ST59 and ST398.Front Microbiol. 2023 Sep 22;14:1266715. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1266715. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37808296 Free PMC article.
-
Genotypic Characterization of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Pigs and Retail Foods in China.Biomed Environ Sci. 2017 Aug;30(8):570-580. doi: 10.3967/bes2017.076. Biomed Environ Sci. 2017. PMID: 28807097
-
Whole-Genome Sequencing and Machine Learning Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus from Multiple Heterogeneous Sources in China Reveals Common Genetic Traits of Antimicrobial Resistance.mSystems. 2021 Jun 29;6(3):e0118520. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.01185-20. Epub 2021 Jun 8. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 34100643 Free PMC article.
-
Livestock-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Asia: an emerging issue?Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2015 Apr;45(4):334-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2014.12.007. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2015. PMID: 25593014 Review.
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus prevalence in food-producing animals and food products in Saudi Arabia: A review.Vet World. 2024 Aug;17(8):1753-1764. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2024.1753-1764. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Vet World. 2024. PMID: 39328450 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Staphylococcus spp. in Salad Vegetables: Biodiversity, Antimicrobial Resistance, and First Identification of Methicillin-Resistant Strains in the United Arab Emirates Food Supply.Foods. 2024 Aug 2;13(15):2439. doi: 10.3390/foods13152439. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39123630 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the multidrug resistance and transmission factors of Staphylococcus aureus at the 'animal-environment-human' interface in the broiler feeding cycle.Front Microbiol. 2025 Feb 12;16:1495676. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1495676. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40012774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartels M. D., Petersen A., Worning P., Nielsen J. B., Larner-Svensson H., Johansen H. K., et al. (2014). Comparing whole-genome sequencing with Sanger sequencing for spa typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 52 4305–4308. 10.1128/jcm.01979-14 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

